Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2014; 6(5): 526-539
Published online Nov 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.526
Published online Nov 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.526
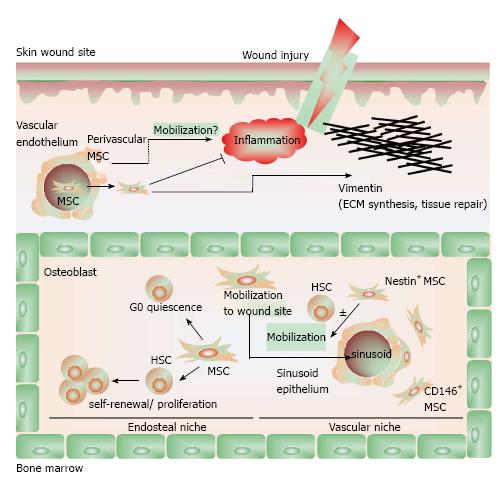
Figure 2 The biology of mesenchymal stem cells.
In the bone marrow, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) aid in constructing the endosteal niche and regulate the homeostasis of HSCs. MSCs maintain HSCs in a state of quiescence defined by self-renewal and proliferation without differentiation. CD146+ MSCs in the vascular niche also maintain HSC homeostasis and, along with Nestin+ MSCs, regulate the mobilization of HSC into the vascular system. In response to inflammatory cues and chemokine gradients, MSCs mobilize out of the bone marrow and to peripheral sites of injury, where they suppress inflammation to facilitate wound healing. MSCs contribute to tissue reconstruction with the production and deposition of vimentin. In is incompletely understood whether perivascular MSCs may also migrate to sites of injury to contribute to wound healing. Adapted from ref [22].
- Citation: Glenn JD, Whartenby KA. Mesenchymal stem cells: Emerging mechanisms of immunomodulation and therapy. World J Stem Cells 2014; 6(5): 526-539
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v6/i5/526.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.526