Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2014; 6(2): 248-255
Published online Apr 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i2.248
Published online Apr 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i2.248
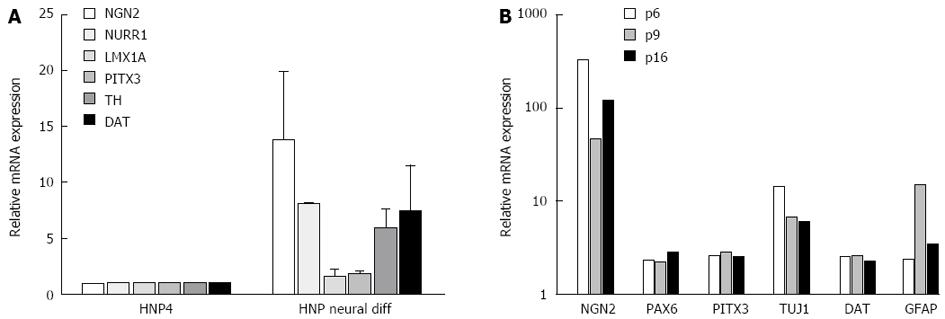
Figure 3 Characterization of dopaminergic neurogenesis in human embryonic stem (H9) derived neural progenitor cells (HNP4) by expression analysis of marker genes.
A: The expression of several specific marker genes (NGN2, NURR1, LMX1A, PITX3, TH and DAT) is displayed as determined by q-RTPCR analysis. The relative gene expression of differentiated neuronal cells (HNP neural diff) at passage 16 was normalized to the house-keeping gene GAPDH and the neural progenitors (HNP4). Three independent experiments were performed and the means + SE are indicated; B: The expression of several specific marker genes (NGN2, PAX6, PITX3, TUJ1, DAT and GFAP) was analyzed 30 d after starting neuronal differentiation of HNP4 cells at passages (p) 6, 9 and 16 by q-RTPCR analysis. The relative gene expression of differentiated neuronal cells was normalized to the house-keeping gene GAPDH and the neural progenitors (HNP4).
- Citation: Liao MC, Diaconu M, Monecke S, Collombat P, Timaeus C, Kuhlmann T, Paulus W, Trenkwalder C, Dressel R, Mansouri A. Embryonic stem cell-derived neural progenitors as non-tumorigenic source for dopaminergic neurons. World J Stem Cells 2014; 6(2): 248-255
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v6/i2/248.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v6.i2.248