Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2014; 6(2): 213-229
Published online Apr 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i2.213
Published online Apr 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i2.213
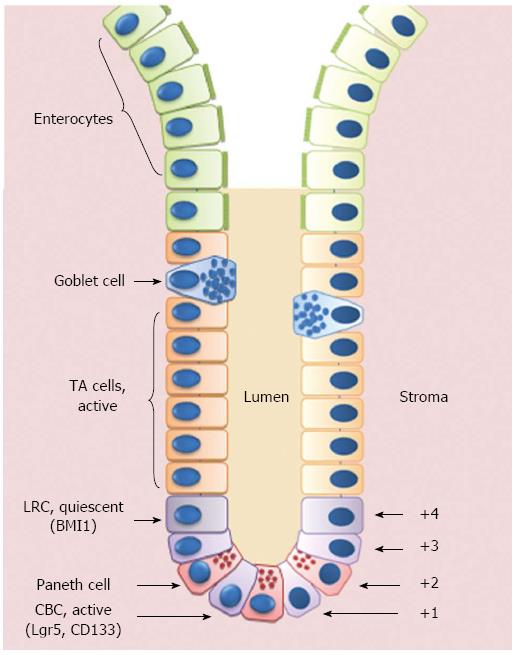
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the crypt/villus axis.
Putative intestinal stem cells (ISCs) reside either at the crypt base, between Paneth cells, as Crypt Base Columnar Cells (CBCs), or in position +4 from the bottom of the crypt, as Label Retaining Cells (LRCs). ISCs give rise to Transit Amplifying (TA) cells that are able to migrate upwards and progressively maturate losing their proliferative capability to become fully-differentiated villous epithelial cells.
- Citation: Piscaglia AC. Intestinal stem cells and celiac disease. World J Stem Cells 2014; 6(2): 213-229
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v6/i2/213.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v6.i2.213