Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2014; 6(2): 120-133
Published online Apr 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i2.120
Published online Apr 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i2.120
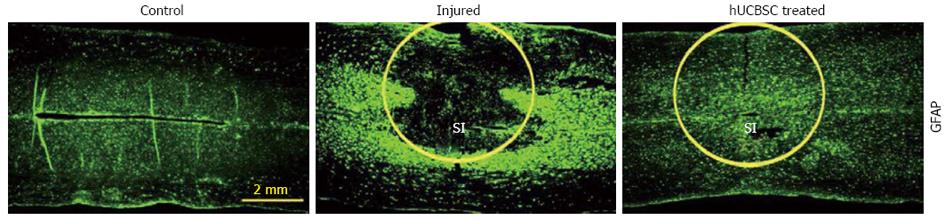
Figure 3 Reduction of inflammation in human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell-treated spinal cords of rats.
Immunohistochemical comparison of control, injured (21 d after spinal cord injury) and human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells-treated spinal cord sections was performed to analyze the expression of reactive astrocytes at the site of injury. GFAP immunoreactivity is more evident and is localized at the lesion epicenter in the injured spinal cords. Astrogliosis is reduced in human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells-treated sections. SI: Site of injury. Neurobiol Dis 2009; 36: 200-212.
- Citation: Dasari VR, Veeravalli KK, Dinh DH. Mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of spinal cord injuries: A review. World J Stem Cells 2014; 6(2): 120-133
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v6/i2/120.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v6.i2.120