Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2013; 5(4): 98-105
Published online Oct 26, 2013. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v5.i4.98
Published online Oct 26, 2013. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v5.i4.98
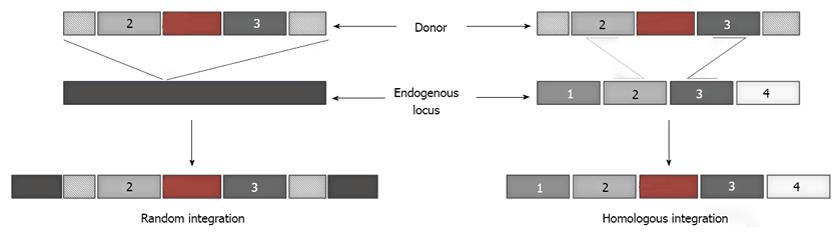
Figure 1 Random and homologous integration.
Introduction of a foreign gene into mammalian cells can either result in its random integration into the endogenous chromosomal DNA, or site-specific integration at the desired location dictated by the homology between the donor DNA and the endogenous target locus.
- Citation: Ramamoorthi K, Curtis D, Asuri P. Advances in homology directed genetic engineering of human pluripotent and adult stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2013; 5(4): 98-105
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v5/i4/98.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v5.i4.98