Copyright
©2012 Baishideng.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2012; 4(5): 35-43
Published online May 26, 2012. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v4.i5.35
Published online May 26, 2012. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v4.i5.35
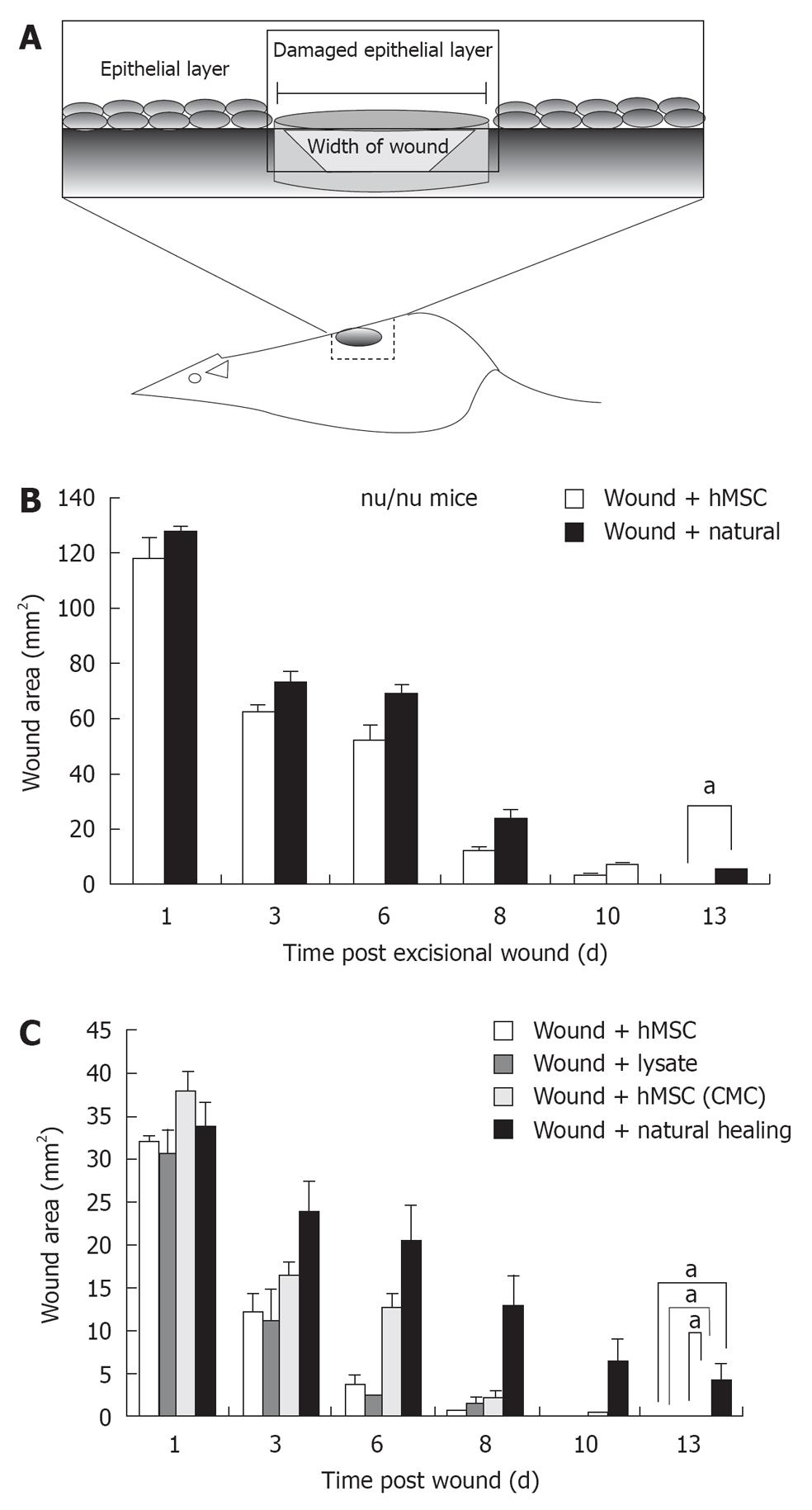
Figure 2 Excisional wound healing using human mesenchymal stem cells injection.
A: Schematic representation of excisional wound axes and the area of interest excised; B: Excisional wound was made aseptically and hMSCs (P < 0.0001, n = 5) were transplanted locally and observed on days 1, 3, 6, 8, 10 and 13; Bar graph represents wound closure over time compared with natural wound closure. Accelerated wound healing by human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs), hMSC lysate and concentrated conditioned medium from hMSC (CMC) in nu/nude mice; C: Macroscopic observation and bar graph representation of hMSC (P < 0.0001, n = 5), hMSC lysate (P < 0.0001, n = 5) and hMSC (CMC) (P < 0.0001, n = 5) injected wounds compared with naturally healing group after 1, 3, 6 8 10 and 13 d in nude mice. aIndicates statistically significant difference. Natural healing is essentially completed on day 14 (not shown).
- Citation: Mishra PJ, Mishra PJ, Banerjee D. Cell-free derivatives from mesenchymal stem cells are effective in wound therapy. World J Stem Cells 2012; 4(5): 35-43
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v4/i5/35.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v4.i5.35