Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2011; 3(8): 70-82
Published online Aug 26, 2011. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v3.i8.70
Published online Aug 26, 2011. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v3.i8.70
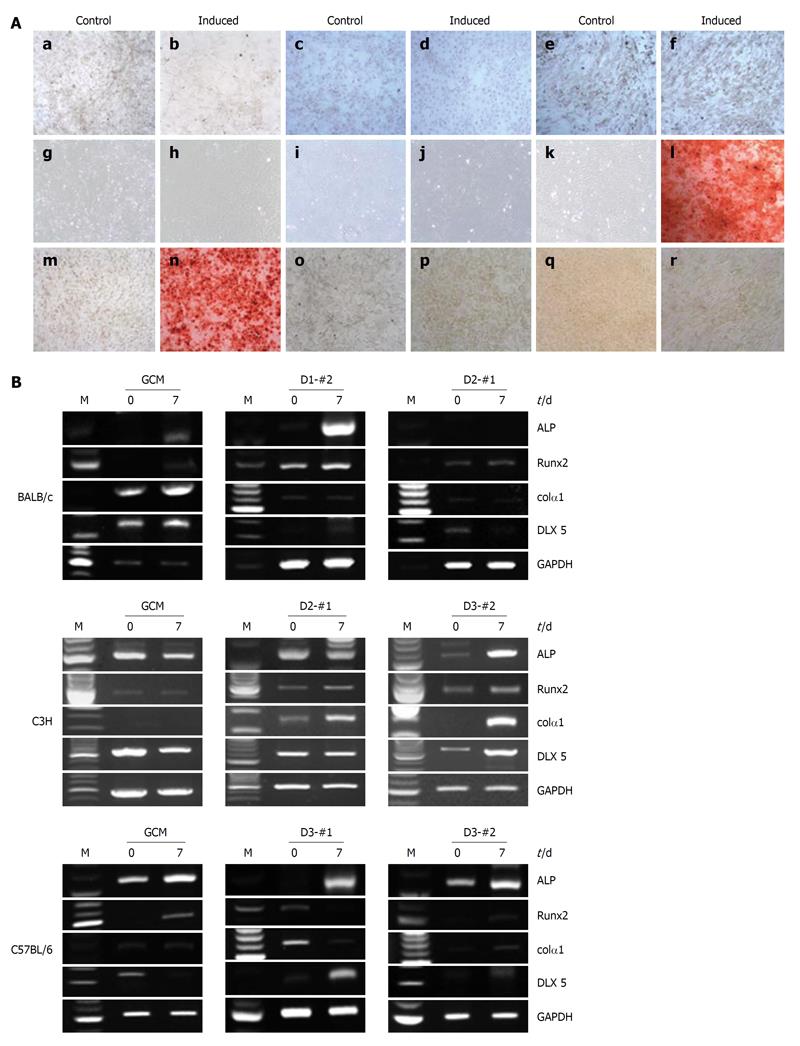
Figure 5 Osteogenic differentiation potentials of the established mouse clonal mesenchymal stem cell lines and nonclonal mesenchymal stem cells.
A: Alizarin Red S staining showed matrix mineralization in the osteogenically differentiated mouse clonal mesenchymal stem cell lines 21 d after osteogenic induction: a and b: BALB/c gradient centrifugation method (GCM); c and d: BALB/c D1-#2; e and f: BALB/c D2-#1; g and h: C3H GCM; i and j: C3H D2-#1; k and l: C3H D3-#2; m and n: C57BL/6 GCM; o and p: C57BL/6 D3-#1; q and r: C57BL/6 D3-#2; B: Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis of osteogenic markers, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), Runx-2, Col1A1, and Distal-less homeobox 5 at days 0 and 7 after osteogenic induction. Glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase was used as an internal control.
- Citation: Jeon MS, Yi TG, Lim HJ, Moon SH, Lee MH, Kang JS, Kim CS, Lee DH, Song SU. Characterization of mouse clonal mesenchymal stem cell lines established by subfractionation culturing method. World J Stem Cells 2011; 3(8): 70-82
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v3/i8/70.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v3.i8.70