Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2011; 3(8): 70-82
Published online Aug 26, 2011. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v3.i8.70
Published online Aug 26, 2011. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v3.i8.70
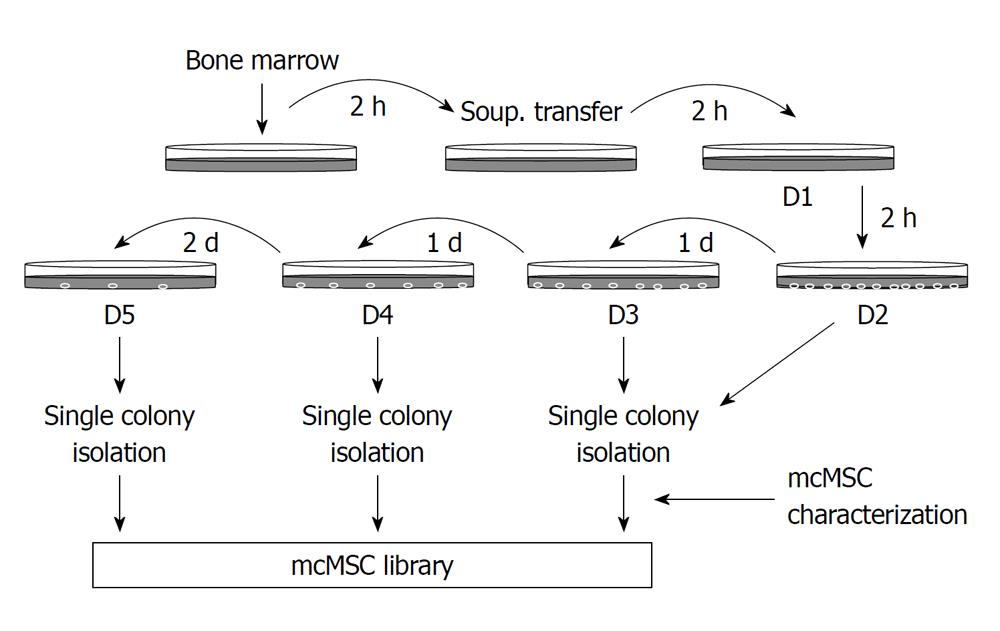
Figure 1 Flow diagram of the “subfractionation culturing method” used to establish mouse clonal mesenchymal stem cell lines.
Mouse bone marrow aspirate was mixed with Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s Medium-low glucose and plated onto a 100-mm cell culture dish. After 2-h incubation, the supernatant only was transferred to a new dish. This procedure was repeated two more times, and then the supernatant was subsequently transferred to cell culture dishes with a 1- or 2-d interval as shown. Each dish was then incubated until single-cell-derived colonies appeared. When colonies of cells were large enough, they were transferred to a six-well plate or 100-mm cell culture dish and then expanded to larger flasks for freezing and further study. Unique mouse clonal mesenchymal stem cell (mcMSC) lines were saved in a mcMSC library.
- Citation: Jeon MS, Yi TG, Lim HJ, Moon SH, Lee MH, Kang JS, Kim CS, Lee DH, Song SU. Characterization of mouse clonal mesenchymal stem cell lines established by subfractionation culturing method. World J Stem Cells 2011; 3(8): 70-82
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v3/i8/70.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v3.i8.70