Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2025; 17(4): 103919
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.103919
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.103919
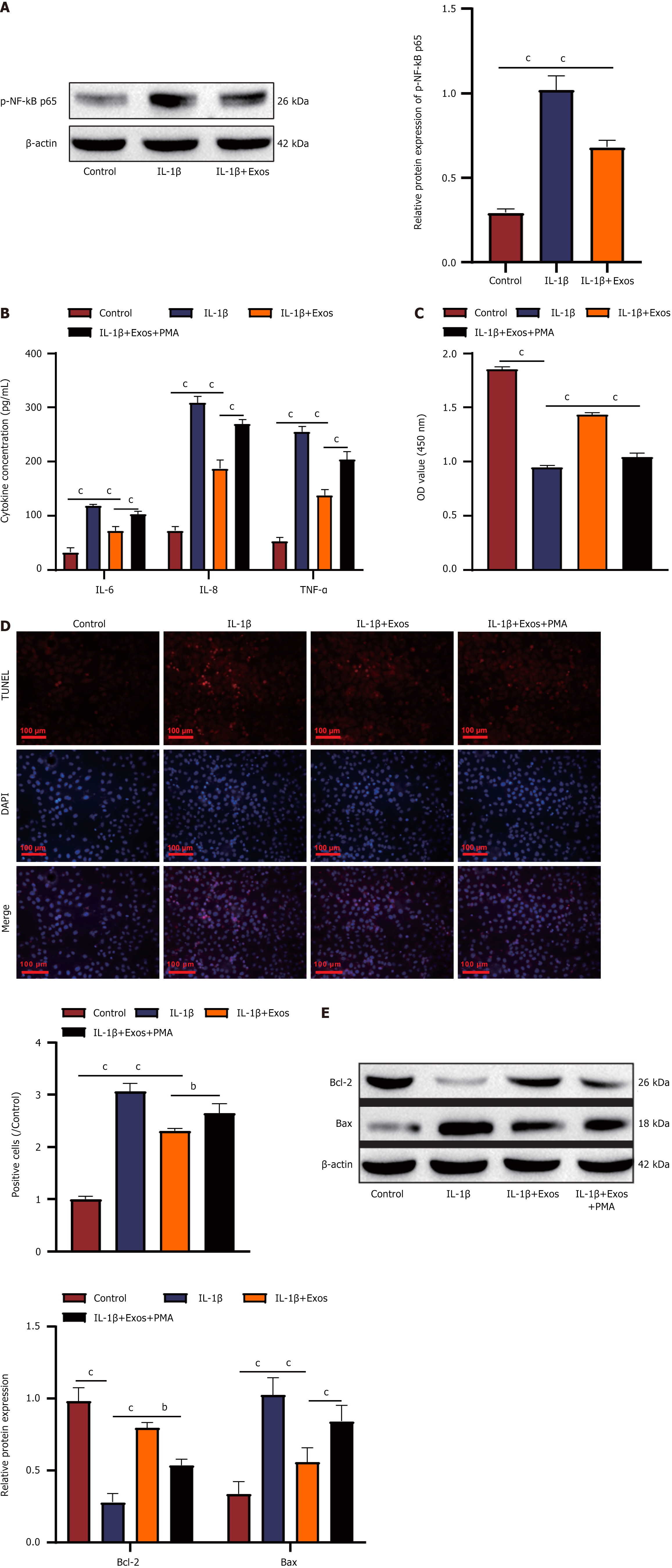
Figure 3 Activation of the nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway attenuates the protective effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on chondrocytes.
A: P-nuclear factor-kappaB p65 expression in CHON-001 cells was determined using western blot analysis; B: Interleukin-6, interleukin-8, and tumor necrosis factor-α levels in CHON-001 cells were determined via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; C: A CCK-8 assay was used to assess the viability of CHON-001 cells; D: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-nick end labelling staining was used to detect apoptosis in CHON-001 cells (scale bar = 100 μm); E: Bcl-2 and Bax apoptosis-related proteins in CHON-001 cells were detected via western blot analysis. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappaB; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; Exos: Exosomes; PMA: Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; OD: Optical density; TUNEL: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-nick end labelling.
- Citation: Chen LQ, Ma S, Yu J, Zuo DC, Yin ZJ, Li FY, He X, Peng HT, Shi XQ, Huang WJ, Li Q, Wang J. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-199a-3p inhibits the MAPK4/NF-κB signaling pathway to relieve osteoarthritis. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(4): 103919
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i4/103919.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.103919