Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2025; 17(4): 103482
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.103482
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.103482
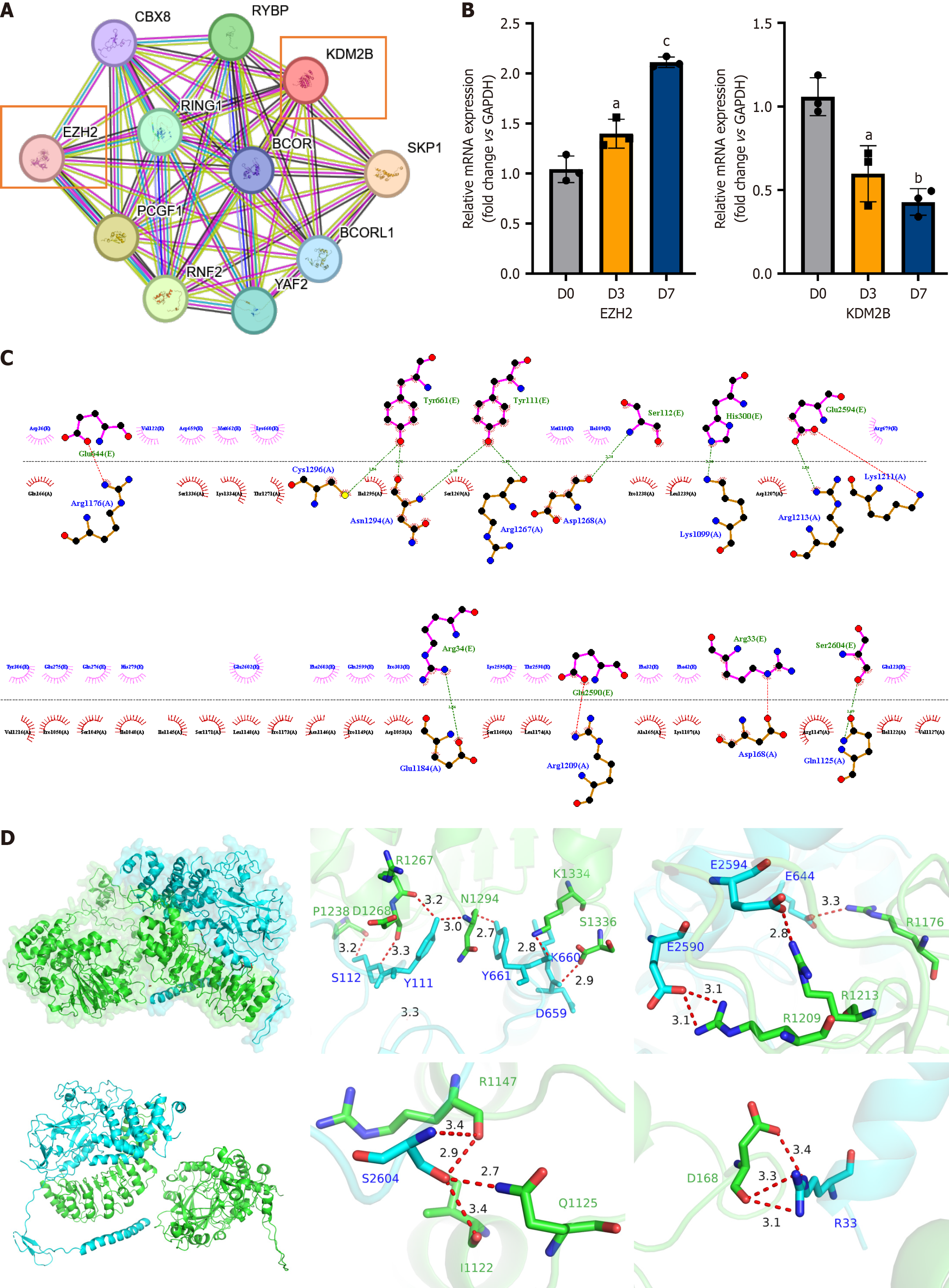
Figure 4 Reduction of enhancer of zeste homolog 2 binding to lysine demethylase 2B promotes osteogenic differentiation of human apical papillary stem cells.
A: The protein-protein interaction network analysis revealed potential direct or indirect interactions between enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) and lysine demethylase 2B (KDM2B); B: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction confirmed that EZH2 expression progressively increased, while KDM2B expression gradually decreased during the induction of osteogenic differentiation in human apical papillary stem cells; C and D: Molecular docking simulations predicted the binding modes and affinities between EZH2 and KDM2B proteins. C illustrates the two-dimensional interactions, while D presents the three-dimensional binding conformations. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test. aP ≤ 0.05, bP ≤ 0.01, cP ≤ 0.001. EZH2: Enhancer of zeste homolog 2; KDM2B: Lysine demethylase 2B.
- Citation: Xu HY, Wang YT, Yang HQ, Cao YY, Fan ZP. EZH2, via an association with KDM2B, modulates osteogenic differentiation of root apical papillary stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(4): 103482
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i4/103482.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.103482