Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2025; 17(4): 103482
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.103482
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.103482
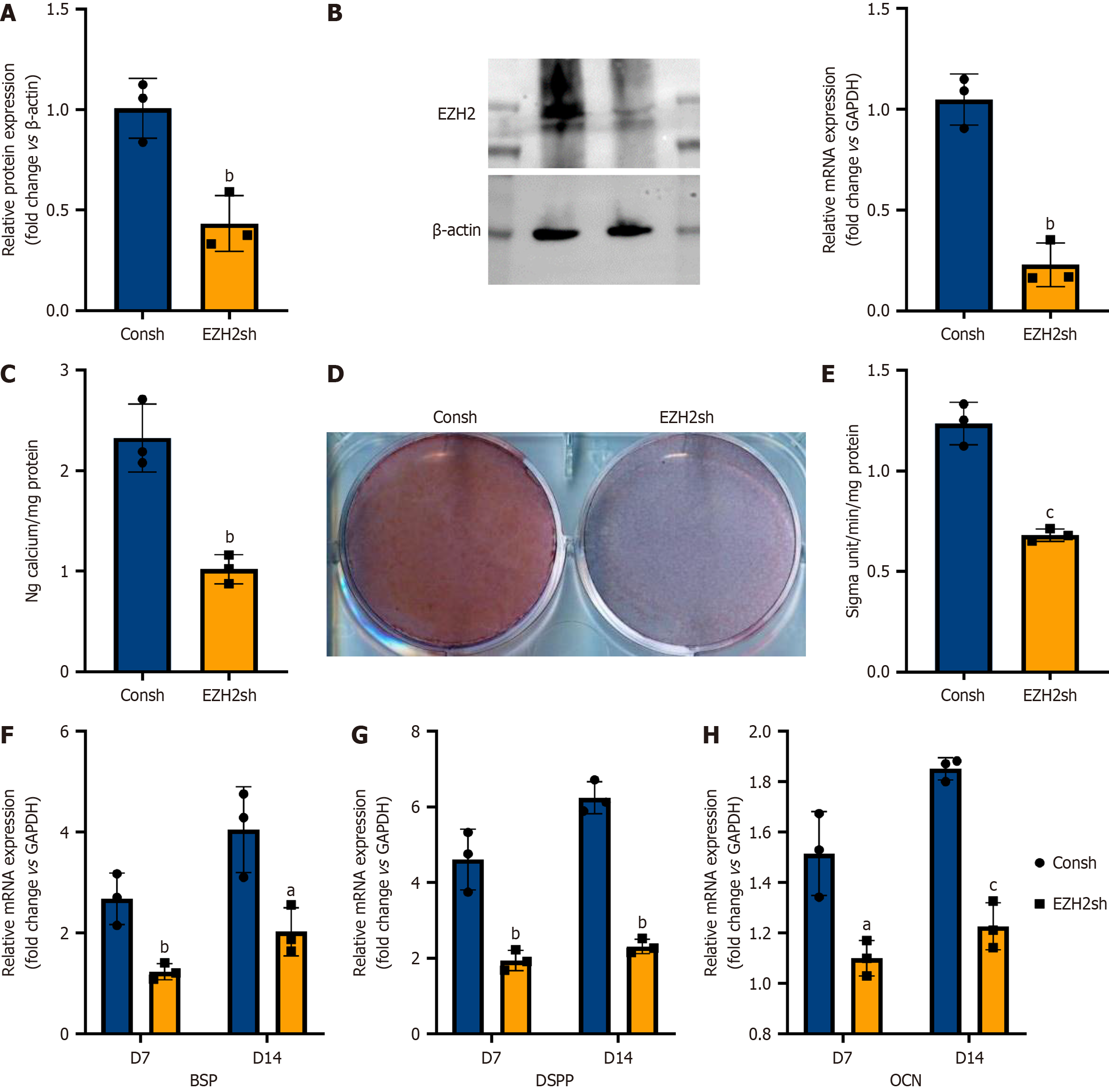
Figure 1 Knockdown of enhancer of zeste homolog 2 inhibits steo/dentinogenic differentiation potential of human apical papillary stem cells.
A: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction showed that the expression of enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) was inhibited in human apical papillary stem cells (hSCAPs); B: Western blot analysis confirmed the knockdown of EZH2 in hSCAPs; C: Knockdown of EZH2 decreased alkaline phosphatase activity in hSCAPs; D and E: Alizarin red staining and quantitative calcium analysis demonstrated that knockdown of EZH2 inhibited mineralization in hSCAPs; F-H: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction showed that knockdown of EZH2 downregulated mRNA expression levels of bone sialoprotein (F), dentin sialophosphoprotein (G), and osteocalcin (H) in hSCAPs. GAPDH and ACTB was used as the internal controls. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test. aP ≤ 0.05, bP ≤ 0.01, cP ≤ 0.001. EZH2: Enhancer of zeste homolog 2; BSP: Bone sialoprotein; DSPP: Dentin sialophosphoprotein; OCN: Osteocalcin.
- Citation: Xu HY, Wang YT, Yang HQ, Cao YY, Fan ZP. EZH2, via an association with KDM2B, modulates osteogenic differentiation of root apical papillary stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(4): 103482
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i4/103482.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.103482