Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2025; 17(4): 103314
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.103314
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.103314
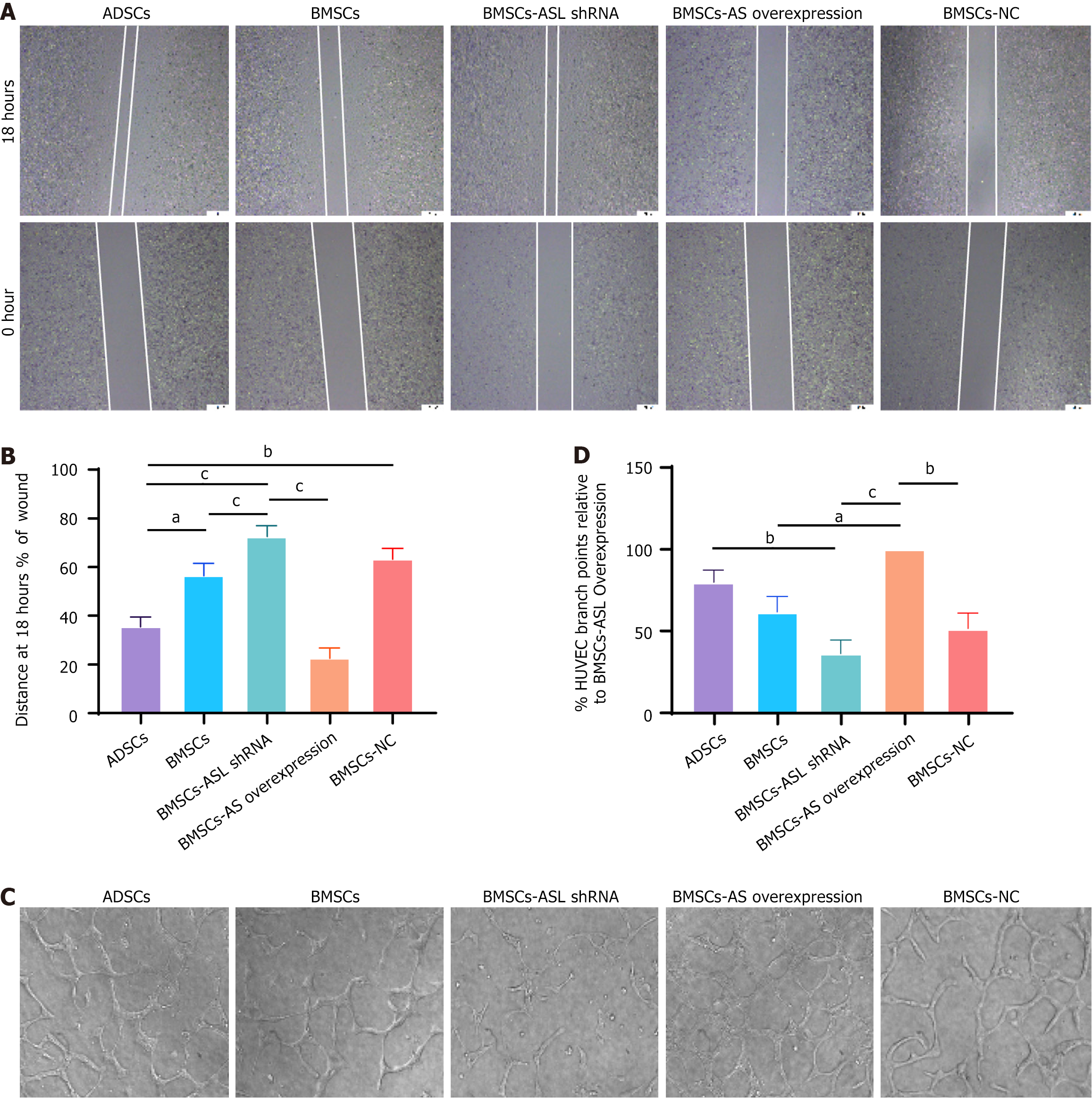
Figure 5 Wound healing and tube formation capacity in adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells from identical older patients cultured in serum-free and hypoxic conditions.
A: Wound healing capacity of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) co-cultured with different mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs); B: Relative quantitative comparison of healing speed analyses (n = 6); C: Representative photomicrographs showing tube formation in HUVECs co-cultured with different MSCs; D: Quantification of endothelial tube junction numbers demonstrated that co-culture with aged patient-derived MSCs promoted HUVECs to form capillary-like structures (n = 6). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. ASL: Arginine succinate lyase; shRNA: Short hairpin RNA; ADSCs: Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells; BMSCs: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells; HUVECs: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells; NC: Negative control.
- Citation: Li JZ, Zhan X, Sun HB, Chi C, Zhang GF, Liu DH, Zhang WX, Sun LH, Kang K. L-arginine from elder human mesenchymal stem cells induces angiogenesis and enhances therapeutic effects on ischemic heart diseases. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(4): 103314
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i4/103314.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.103314