Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2025; 17(4): 101290
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.101290
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.101290
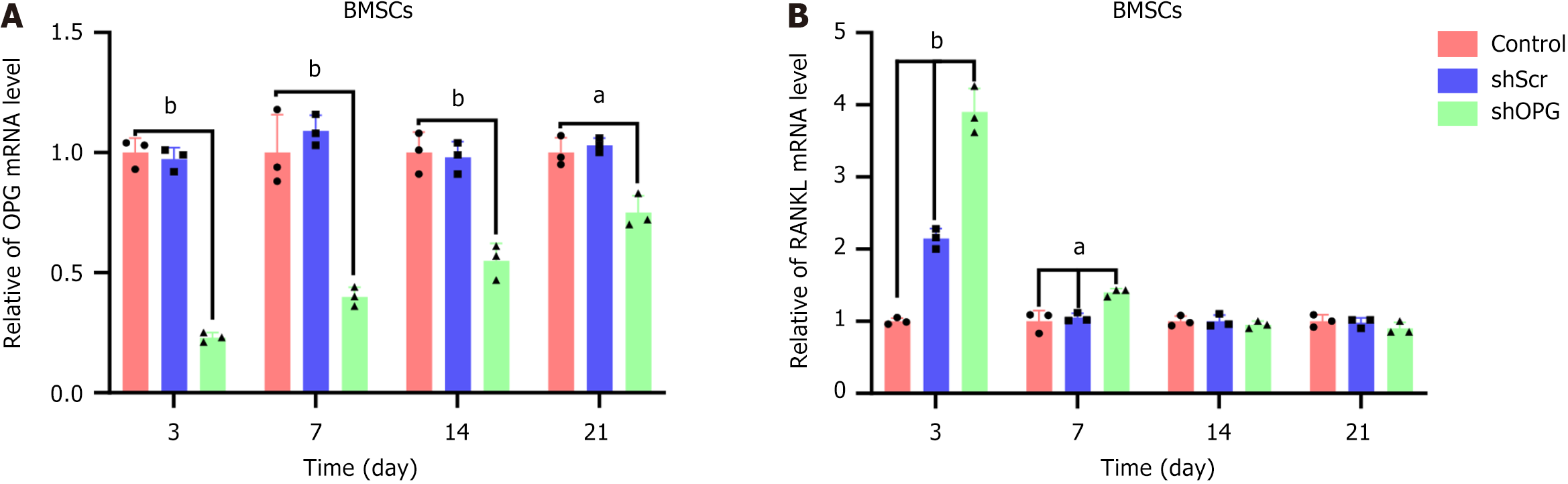
Figure 3 The mRNA levels of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand and osteoprotegerin genes in each group.
A and B: On the 3rd, 7th, 14th, and 21st day post-transfection, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to evaluate the mRNA levels of osteoprotegerin (OPG) (A) and receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL) (B) in each group. The experimental group, “shOPG”, represents OPG gene-silenced bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) transfected with shOPG, while the control groups, “shScr” and “control”, represent BMSCs transfected with a scramble vector and untreated BMSCs, respectively. Compared to the shScr and control groups, RANKL was upregulated in shOPG-transfected BMSCs, particularly on day 3. Conversely, OPG expression was downregulated in shOPG-transfected BMSCs compared to the shScr and control groups (mean ± SEM, n = 3 experiments). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. BMSC: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell; OPG: Osteoprotegerin; RANKL: Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand.
- Citation: Wei SG, Chen HH, Xie LR, Qin Y, Mai YY, Huang LH, Liao HB. RNA interference-mediated osteoprotegerin silencing increases the receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand/osteoprotegerin ratio and promotes osteoclastogenesis. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(4): 101290
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i4/101290.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.101290