Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2025; 17(4): 100359
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.100359
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.100359
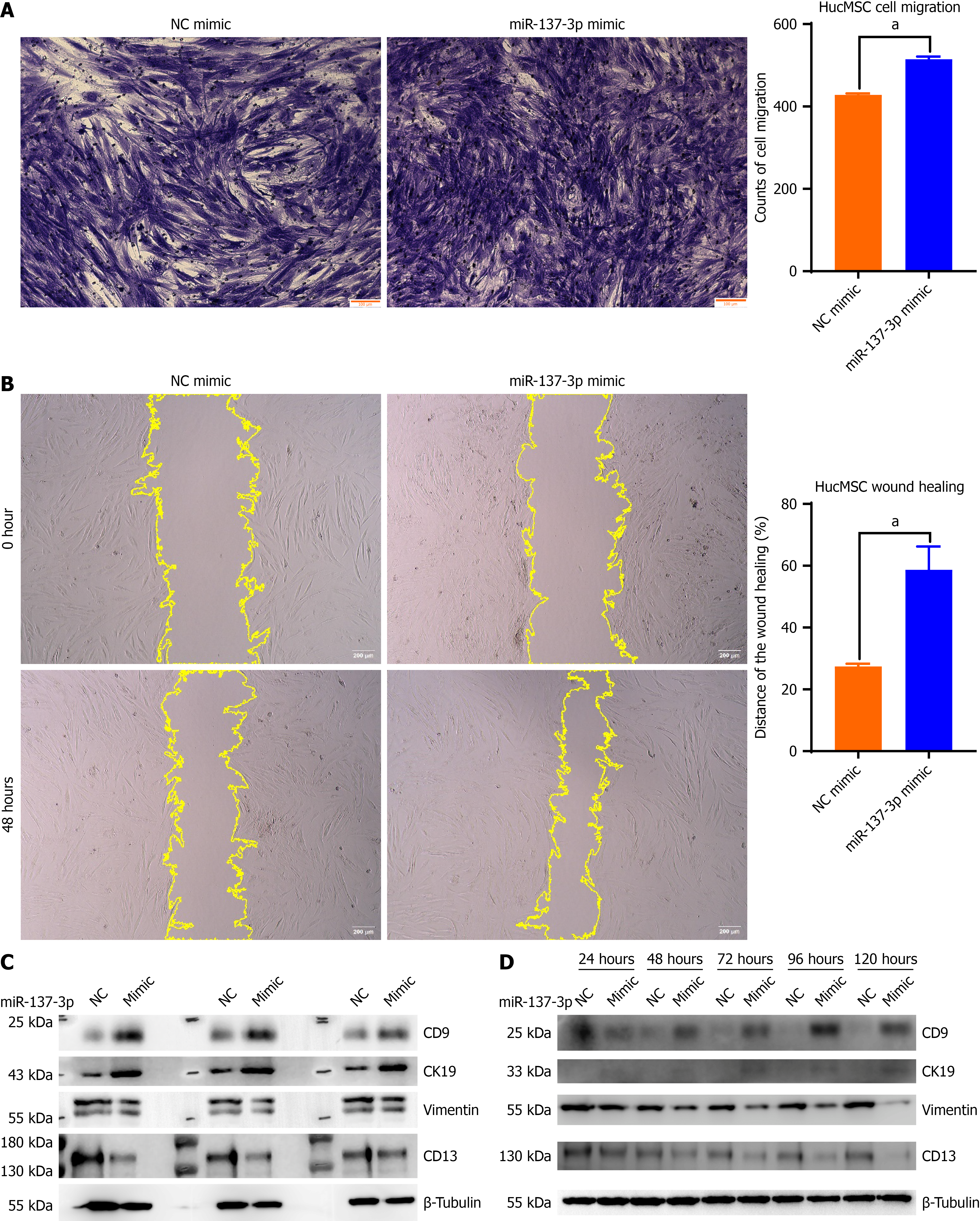
Figure 2 miR-137-3p augmented the migratory and differentiation capabilities of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell into endometrial epithelial cell.
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells were subjected to transfection with miR-137-3p mimic or negative control. A: Transwell assays were employed to assess cellular migration. Scale bar = 100 μm, n = 3; B: Wound healing assays quantified the migratory capacity of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell. Scale bar = 200 μm, n = 3; C: The protein levels of CD9, CK19, vimentin, and CD13 were elucidated using western blotting; D: Western blot analysis elucidating the protein levels of CD9, CK19, vimentin, and CD13. The results are depicted as mean ± SD. aP < 0.0001 vs negative control mimic group, n = 3. HucMSC: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell; NC: Negative control.
- Citation: Zhang WY, Liu SM, Wang HB, Deng CY. Exosomal miR-137-3p targets UBE3C to activate STAT3, promoting migration and differentiation into endometrial epithelial cell of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells under hypoxia. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(4): 100359
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i4/100359.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.100359