Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2025; 17(4): 100359
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.100359
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.100359
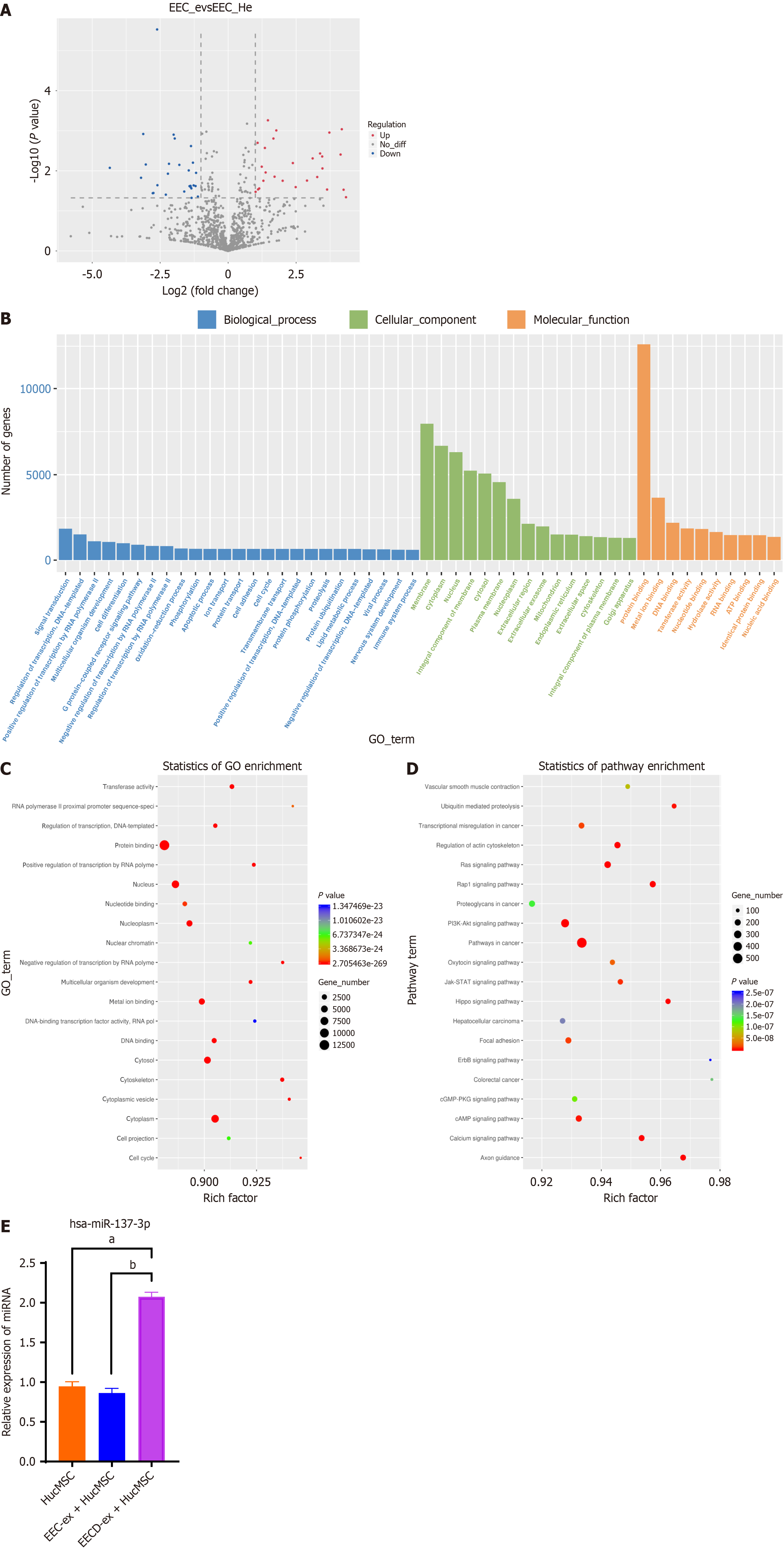
Figure 1 miR-137-3p was markedly elevated in human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell co-cultured with hypoxia-compromised endometrial epithelial cell-derived exosomes.
The culture medium from healthy endometrial epithelial cell (EEC-ex) or hypoxia-compromised EEC (EECD-ex) was gathered for the extraction of exosomes, which were subsequently incorporated into a co-culture system with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell. A: A volcano plot illustrating the differentially expressed microRNAs in human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell subjected to EEC-ex or EECD-ex; B-D: Gene Ontology analysis (B and C) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis (D) of the target genes associated with differentially expressed microRNAs, as assessed by RNA sequencing; E: The quantification of miR-137-3p expression levels via reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Data are represented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.0001 vs human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell group, bP < 0.0001 vs healthy endometrial epithelial cell + human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell group, n = 3. EEC: Endometrial epithelial cell; GO: Gene Ontology; HucMSC: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell; EEC-ex: Healthy endometrial epithelial cell; EECD-ex: Hypoxia-compromised endometrial epithelial cell.
- Citation: Zhang WY, Liu SM, Wang HB, Deng CY. Exosomal miR-137-3p targets UBE3C to activate STAT3, promoting migration and differentiation into endometrial epithelial cell of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells under hypoxia. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(4): 100359
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i4/100359.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.100359