Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Mar 26, 2025; 17(3): 102088
Published online Mar 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i3.102088
Published online Mar 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i3.102088
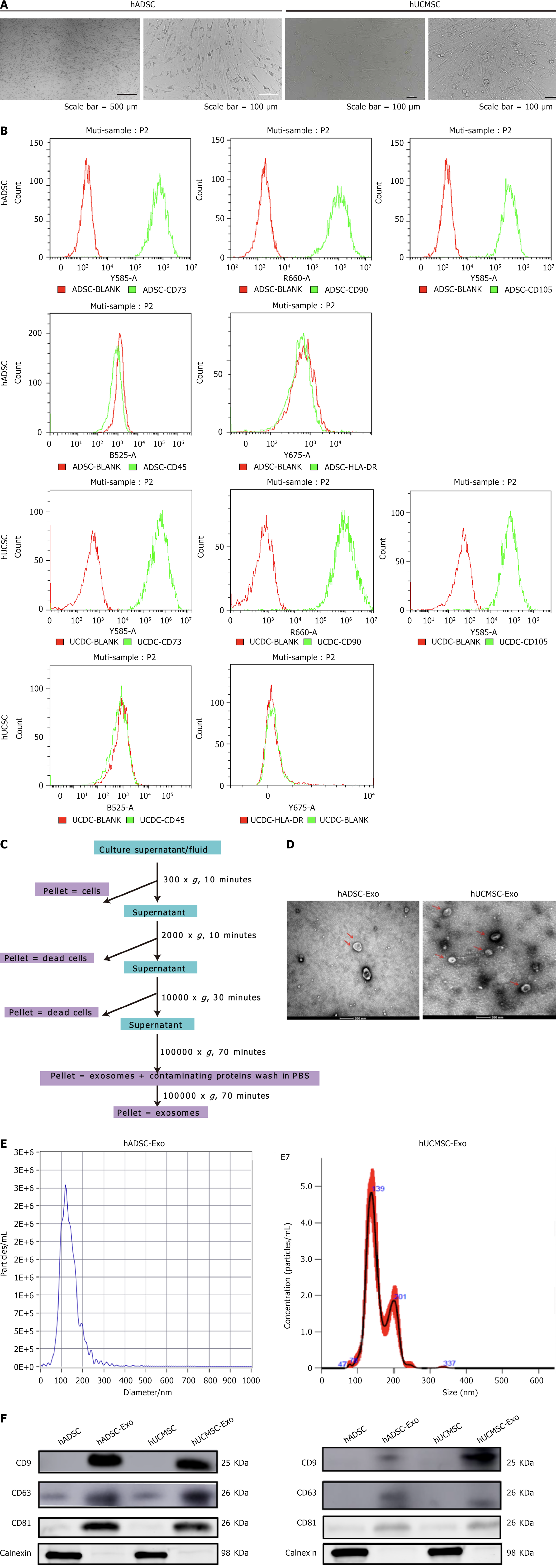
Figure 1 Identification of exosome from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell and human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell.
A: Morphology of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell (hADSC) and human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell (hUCMSC); B: Analysis of surface markers on hADSCs and hUCMSCs showed high CD105, CD90, and CD73 expression, but negative HLA-DR and CD45 expression; C: Schematic presentation of exosome isolated from hADSC and hUCMSC by differential ultracentrifugation; D: By TEM, purified hADSC exosome (hADSC-Exo) and hUCMSC exosome (hUCMSC-Exo) exhibit cup-like morphologies; E: Nanoparticle analysis of hADSC-Exo and hUCMSC-Exo; F: hADSC-Exo and hUCMSC-Exo express CD63, CD9, CD81 and calnexin is not expressed. hADSC: Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell; hUCMSC: Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell; hADSC-Exo: Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome; hUCMSC-Exo: Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome.
- Citation: Fu Y, Han YT, Xie JL, Liu RQ, Zhao B, Zhang XL, Zhang J, Zhang J. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes enhance the development of hair follicle to ameliorate androgenetic alopecia. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(3): 102088
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i3/102088.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i3.102088