Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2025; 17(2): 102091
Published online Feb 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i2.102091
Published online Feb 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i2.102091
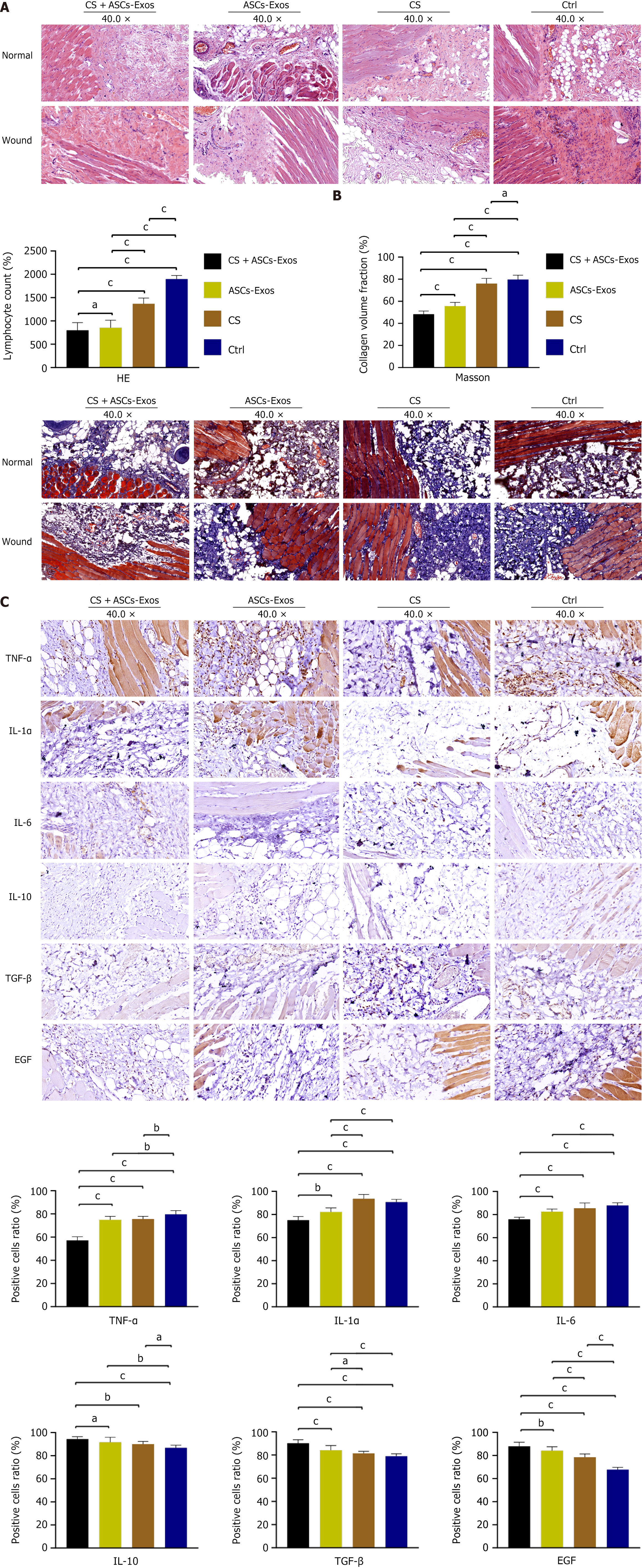
Figure 3 Histological and immunohistochemical analysis of wound healing.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin: Chitosan (CS) + adipose-derived stem cell exosomes (ASC-Exos) treatment reduced lymphocyte infiltration and vascular density compared to normal tissue. ASC-Exos alone showed similar effects but with prominent glands. CS group displayed increased smooth muscle, fibroblasts, and vascular structures. Control group exhibited extensive fibroblast presence, disorganized vasculature, and marked lymphocyte infiltration; B: Masson: CS+ASC-Exos: In the wound, numerous muscle fibers are interspersed with a small amount of collagen fibers, and the quantity and distribution of collagen fibers and muscle fibers are consistent with those in normal tissue. ASC-Exos group showed mild collagen increase. CS and control groups demonstrated excessive collagen deposition and muscle fiber formation. Collagen volume fraction was significantly lower in CS + ASC-Exos group; C: Immunohistochemical: CS + ASC-Exos group showed elevated interleukin (IL)-10, transforming growth factor-β, and epidermal growth factor expression, with reduced tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-1α, and IL-6 levels compared to other groups. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. ASC-Exos: Adipose-derived stem cell exosomes; CS: Chitosan; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; TGF: Transforming growth factor; EGF: Epidermal growth factor.
- Citation: Xu L, Liu D, Yun HL, Zhang W, Ren L, Li WW, Han C. Effect of adipose-derived stem cells exosomes cross-linked chitosan-αβ-glycerophosphate thermosensitive hydrogel on deep burn wounds. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(2): 102091
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i2/102091.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i2.102091