Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2025; 17(2): 101395
Published online Feb 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i2.101395
Published online Feb 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i2.101395
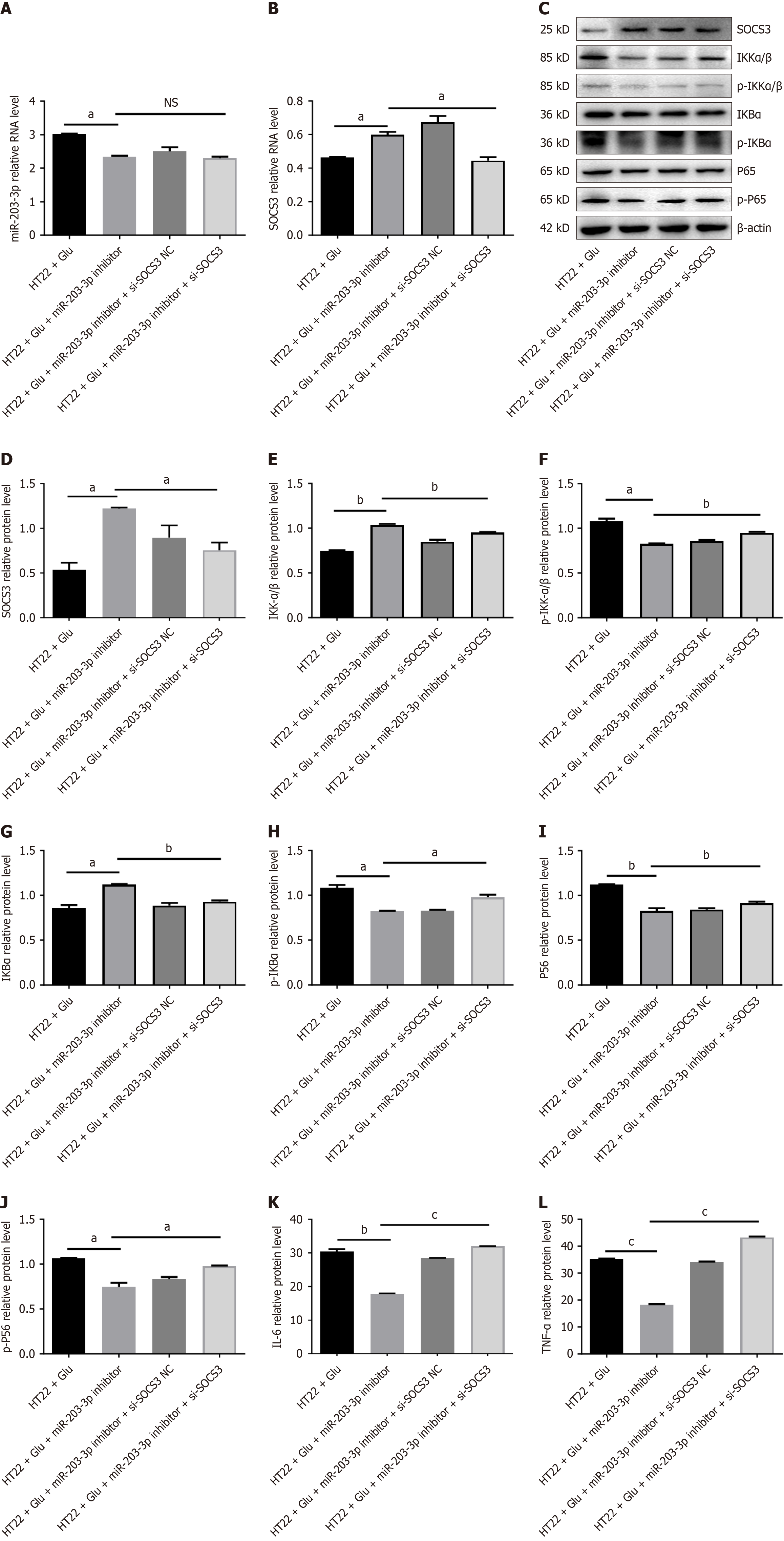
Figure 5 Downregulation of miR-203-3p and suppression of cytokine signaling 3 can reinstate an inflammatory phenotype.
A: Schematic representation of the experimental design of HT22 cells co-transfected with the miR-203-3p inhibitor and si-suppression of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) or si-NC; B: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of SOCS3 mRNA expression in HT22 cells following co-transfection; C and D: Western blot analysis of SOCS3 protein levels in HT22 cells under the same conditions as Figure 5C; E-J: Western blot analysis of nuclear factor kappaB pathway markers in HT22 cells co-transfected with miR-203-3p inhibitor and si-SOCS3 or si-NC; K and L: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay measurements of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α levels in the supernatant of HT22 cells co-transfected as in Figure 5C. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, NS: No significance. SOCS3: Suppression of cytokine signaling 3; IKKα/β: Inhibitor of kappa B kinase alpha/beta; p-IKKα/β: Phospho-inhibitor of kappa B kinase alpha/beta; IKBα: Nuclear factor kappaB inhibitor alpha; p-IKBα: Phospho-nuclear factor kappaB inhibitor alpha; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-6: Interleukin-6.
- Citation: Wang W, Yin J. Exosomal miR-203 from bone marrow stem cells targets the SOCS3/NF-κB pathway to regulate neuroinflammation in temporal lobe epilepsy. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(2): 101395
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i2/101395.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i2.101395