Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2025; 17(2): 101030
Published online Feb 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i2.101030
Published online Feb 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i2.101030
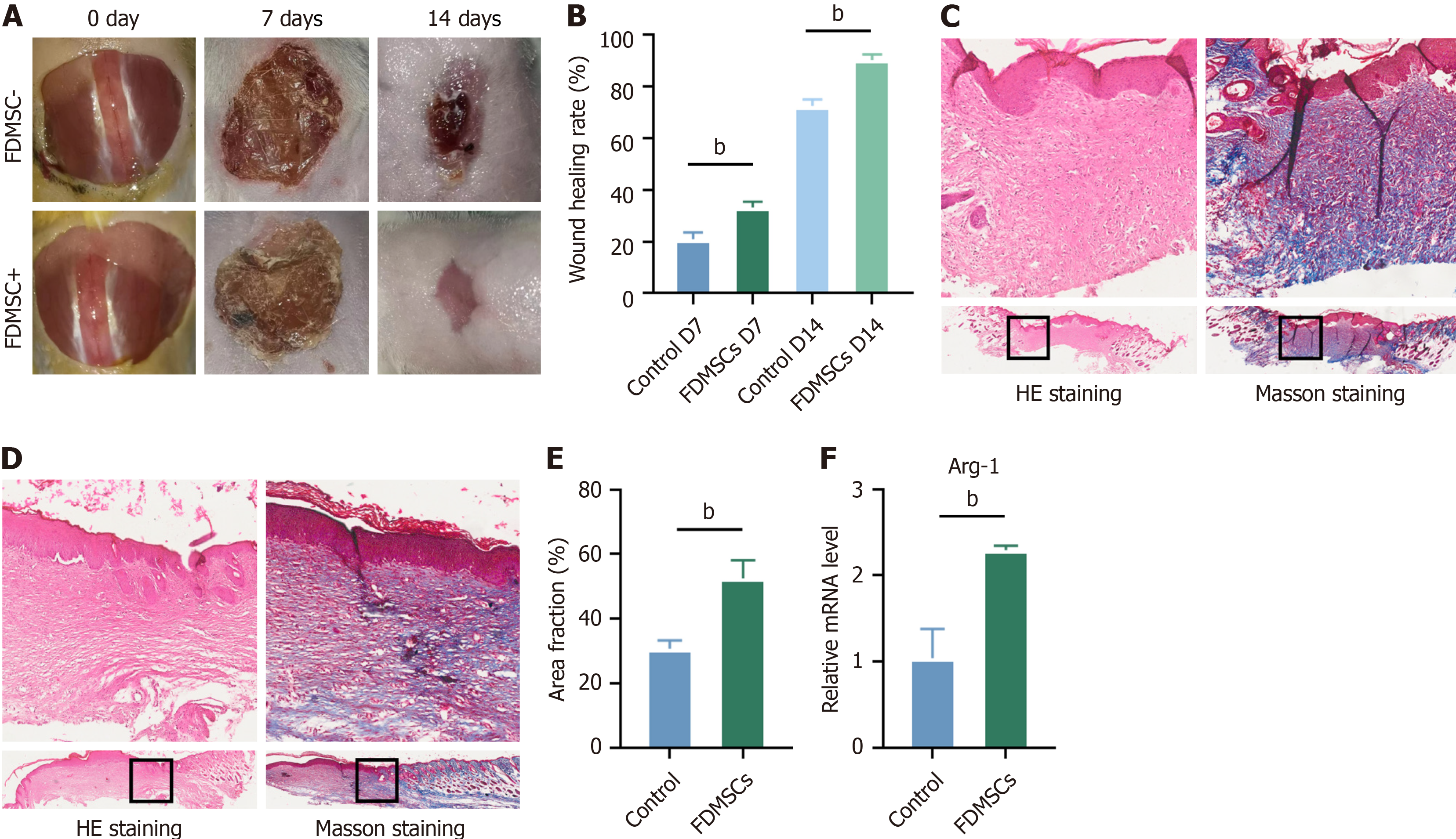
Figure 4 Evaluation of wound healing and tissue analysis in mice following thoracoscopic surgery.
A: Mice were euthanized on postoperative days 0, 7, and 14; wound healing was photographed and documented; B: Analysis of wound healing rate; C and D: Hematoxylin and eosin and Masson’s trichrome staining of traumatized skin on day 14 (× 40 magnification); E: The area of blue-stained collagen in Masson’s trichrome-stained sections was quantified using ImageJ software and statistically analyzed; F: Mouse trauma tissue extracted on day 14 for quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction analysis to detect arginase-1 expression. bP < 0.01. HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; Arg-1: Arginase-1; FDMSC: Fetal dermal mesenchymal stem cell.
- Citation: Xia ZY, Wang Y, Shi N, Lu MQ, Deng YX, Qi YJ, Wang XL, Zhao J, Jiang DY. Fetal mice dermal mesenchymal stem cells promote wound healing by inducing M2 type macrophage polarization. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(2): 101030
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i2/101030.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i2.101030