Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Jan 26, 2025; 17(1): 98349
Published online Jan 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i1.98349
Published online Jan 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i1.98349
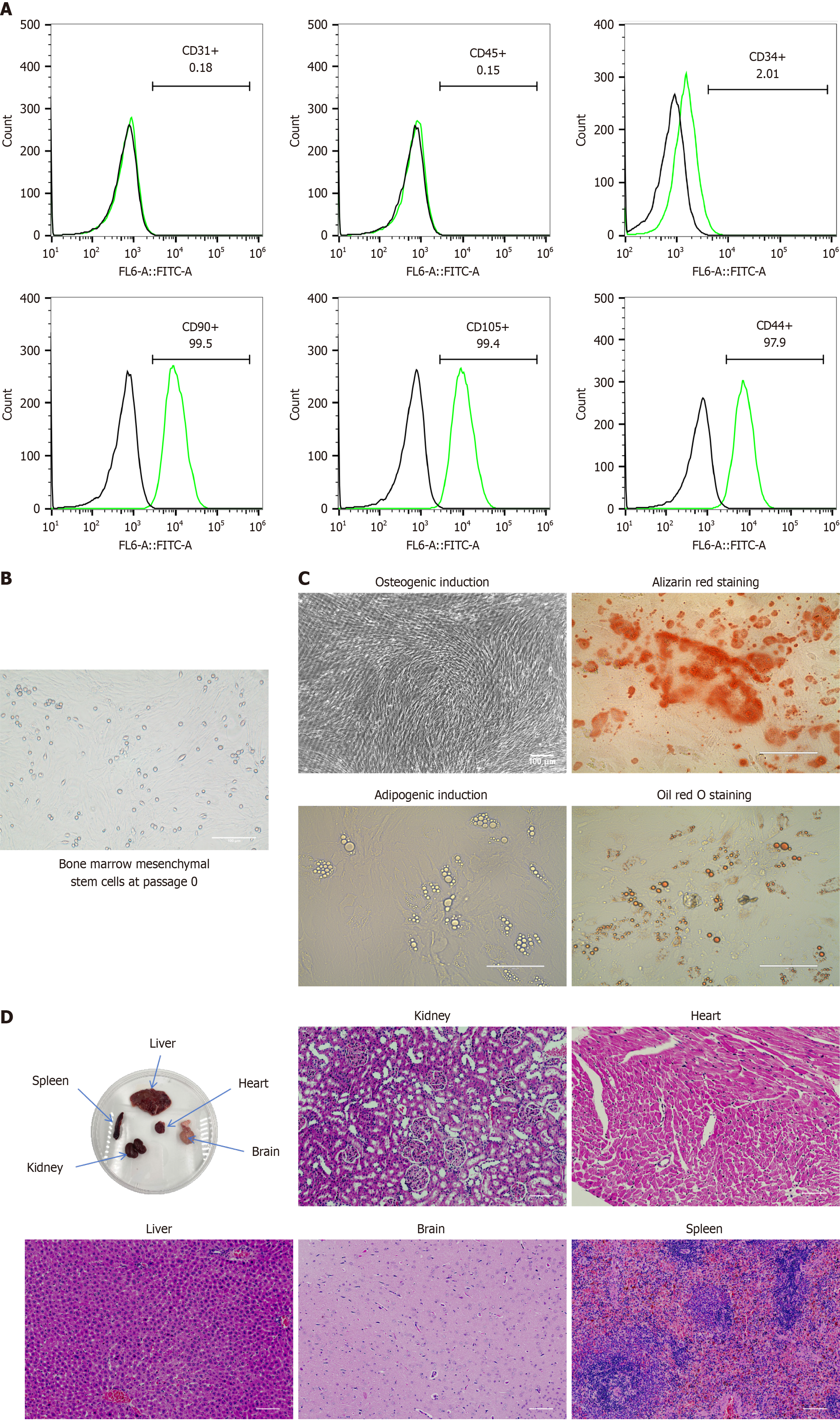
Figure 1 Characterization, morphology, differentiation capacity, and safety of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.
A: Flow cytometric analysis of CD90, CD44, CD105, CD34, CD45, and CD31 expression in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs). The black lines represent isotype controls, whereas the green lines represent the levels of surface markers; B: Representative optical microscopy image of passage 0 BMSCs cultured for 5 d in plastic cell culture flasks (scale bar = 100 μm); C: Multilineage differentiation potential of BMSCs. BMSCs differentiate into mature adipocytes and osteoblasts upon induction. Lipid droplets and bone trabecular structures were observed under a light microscope and stained with Oil Red O and Alizarin Red to detect adipocytes and osteoblasts derived from BMSCs (scale bar = 100 μm); D: Gross appearance images of primary organs in rat models after BMSC transplantation, as assessed via hematoxylin and eosin staining to examine tissue structures (scale bar = 100 μm).
- Citation: Yang J, Yuan J, Wen YQ, Wu L, Liao JJ, Qi HB. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote uterine healing by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway and modulating inflammation in rat models. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(1): 98349
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i1/98349.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i1.98349