Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Jan 26, 2025; 17(1): 101485
Published online Jan 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i1.101485
Published online Jan 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i1.101485
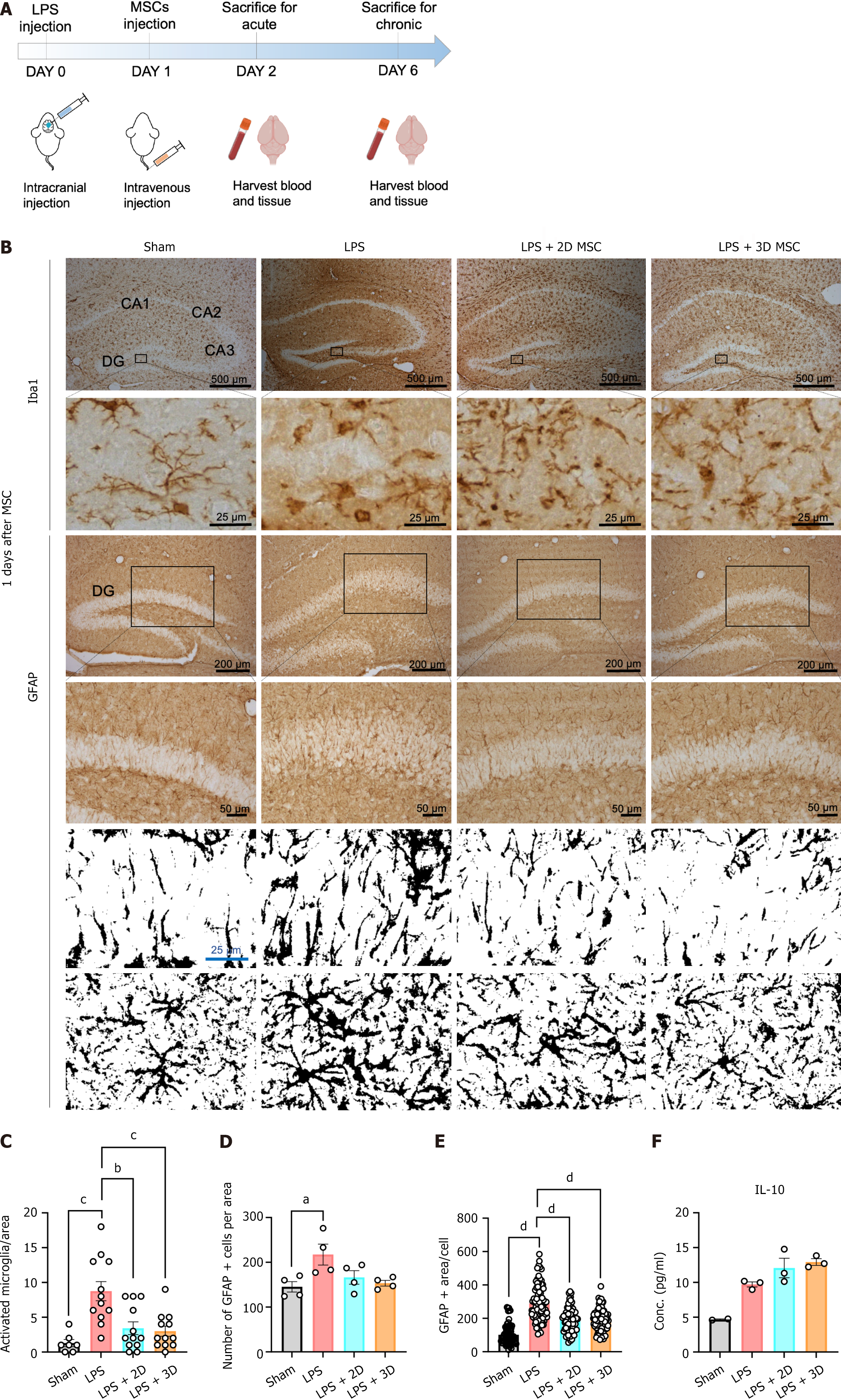
Figure 4 Application of both two-dimensional and three-dimensional-cultured mesenchymal stromal cells reduces the inflammatory response in murine acute lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation model.
A: Representation of the experimental scheme; B: Immunohistochemistry staining of ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1, microglia marker, and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), an astrocyte marker, in the hippocampal region after induction of acute neuroinflammation with lipopolysaccharide. Enlarged inset windows represent a small representative portion of top layer in each staining. The black/white images of GFAP were contrasted by flipping the stained and unstained sections to black and white. Scale bars represent 25 μm, 50 μm, 200 μm, 500 μm; C: Quantify the area of activated microglia in acute model (n = 3-4, Kruskal-Wallis One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001); D: Quantify the number of positive GFAP cells per area in acute model (n = 4, Kruskal-Wallis One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons, aP < 0.05); E: Quantify the area of positive GFAP per cell in acute model (n = 3-4, Kruskal-Wallis One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons, dP < 0.0001); F: Measurement of plasma interleukin-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine, in the blood of acute inflammation model by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (n = 3 independent experiment, Kruskal-Wallis One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons). LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; MSC: Mesenchymal stromal cell; Iba1: Ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1; GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein; 2D: Two-dimensional; 3D: Three-dimensional; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Kim OH, Kang H, Chang ES, Lim Y, Seo YJ, Lee HJ. Extended protective effects of three dimensional cultured human mesenchymal stromal cells in a neuroinflammation model. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(1): 101485
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i1/101485.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i1.101485