Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2024; 16(8): 811-823
Published online Aug 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i8.811
Published online Aug 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i8.811
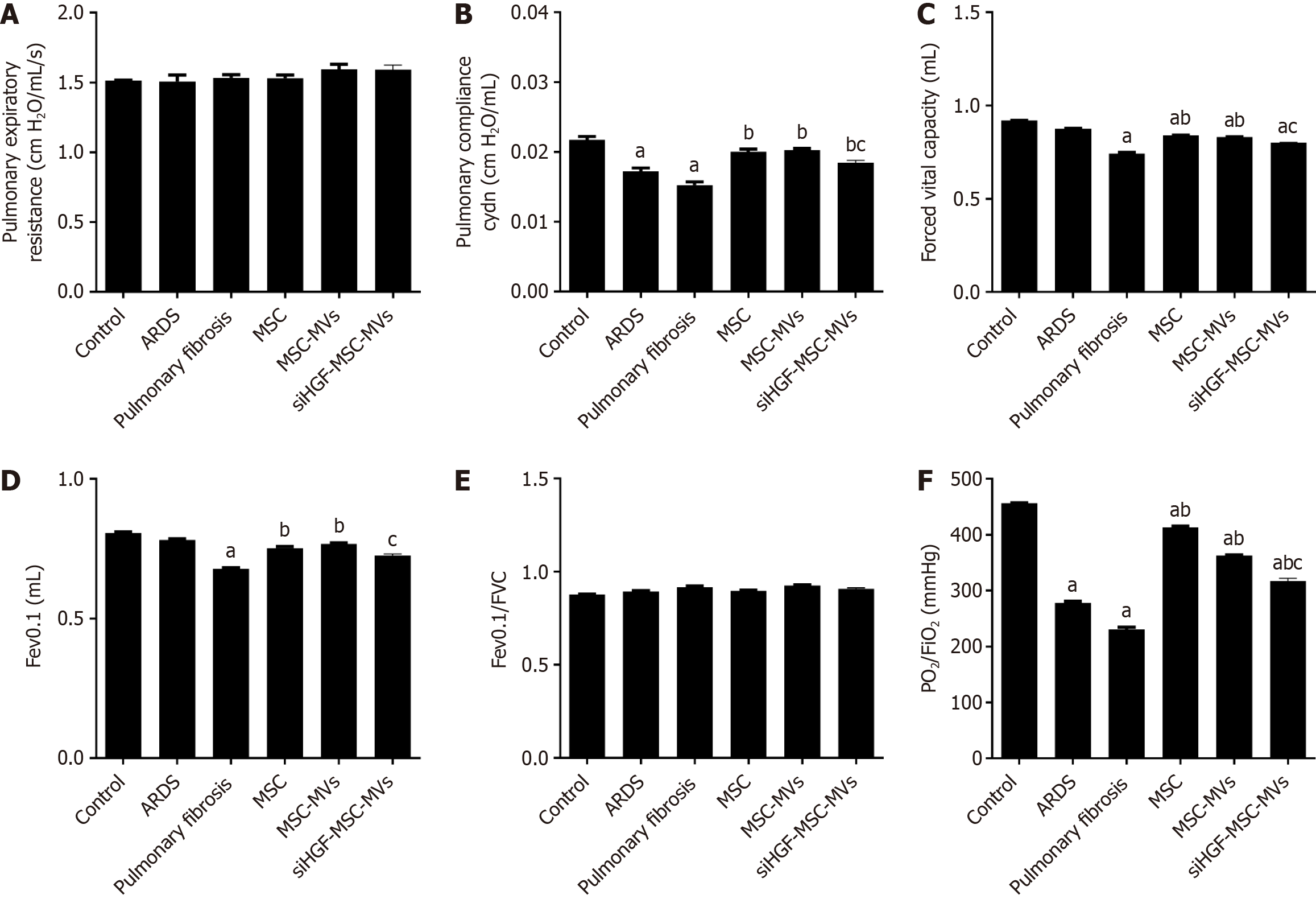
Figure 7 Effects of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived microvesicles on respiratory mechanics and lung functions in acute respiratory distress syndrome pulmonary fibrosis mouse models.
A: Pulmonary expiratory resistance; B: Pulmonary compliance; C: Forced expiratory volume in 0.1 seconds (Fev0.1); D: Forced vital capacity (FVC), E: Fev0.1/FVC; F: Pressure of oxygen (PO2)/oxygen inhalation (FiO2); G: Transmission and scanning electron microscopy were performed on purified mesenchymal stromal cell-derived microvesicles (MSC-MVs) to reveal their spheroid morphologies and confirm their sizes. aP < 0.05, vs the control group; bP < 0.05, vs the pulmonary fibrosis group; cP < 0.05, vs the MSC-MVs group (n = 6). Control, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), pulmonary fibrosis, MSC, MSC-MVs and low hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-MSC-MVs represent the control group, ARDS group, pulmonary fibrosis group, MSC group, MSC-MVs group and low HGF-MSC-MVs group, respectively.
- Citation: Chen QH, Zhang Y, Gu X, Yang PL, Yuan J, Yu LN, Chen JM. Microvesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells inhibit acute respiratory distress syndrome-related pulmonary fibrosis in mouse partly through hepatocyte growth factor. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(8): 811-823
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i8/811.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i8.811