Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2024; 16(6): 708-727
Published online Jun 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.708
Published online Jun 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.708
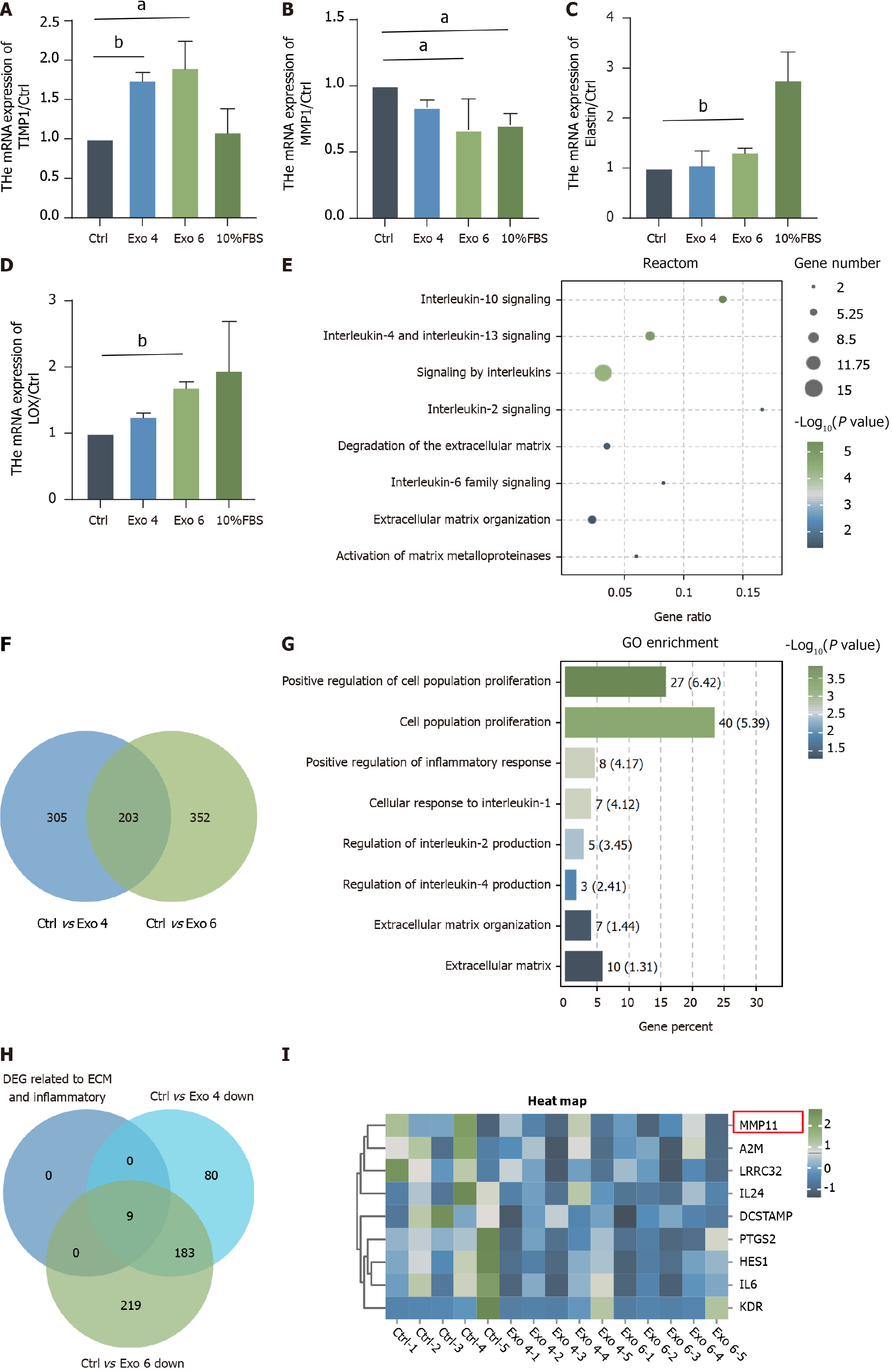
Figure 7 Effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosome on the gene expression profile of human primary vaginal fibroblasts.
A-D: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was performed to evaluate the mRNA levels of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloprotease 1, matrix metalloproteinase 1, elastin and lysyl oxidase; E: Venn diagrams were generated to show the shared differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from the comparison of the group treated with 4 μg/mL versus the Exo-depleted group and the other group exposed to 4 μg/mL versus the Exo-depleted group [fold change (FC) > 1.5, P < 0.05]. F and G: Reactome analysis (F) and Gene Ontology (G) analysis of the 203 overlapping genes; H: Venn diagrams showed DEGs about extracellular matrix (ECM) and inflammatory (FC > 1.5, P < 0.05); I: The heatmap depicting the 11 genes most related to inflammatory and ECM organization processes. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. TIMP1: Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloprotease 1; MMP1: Matrix metalloproteinase 1; LOX: Lysyl oxidase; GO: Gene Ontology; FBS: Fetal bovine serum; Exo: Exosome.
- Citation: Xu LM, Yu XX, Zhang N, Chen YS. Exosomes from umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells promote the collagen production of fibroblasts from pelvic organ prolapse. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(6): 708-727
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i6/708.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.708