Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2024; 16(6): 708-727
Published online Jun 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.708
Published online Jun 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.708
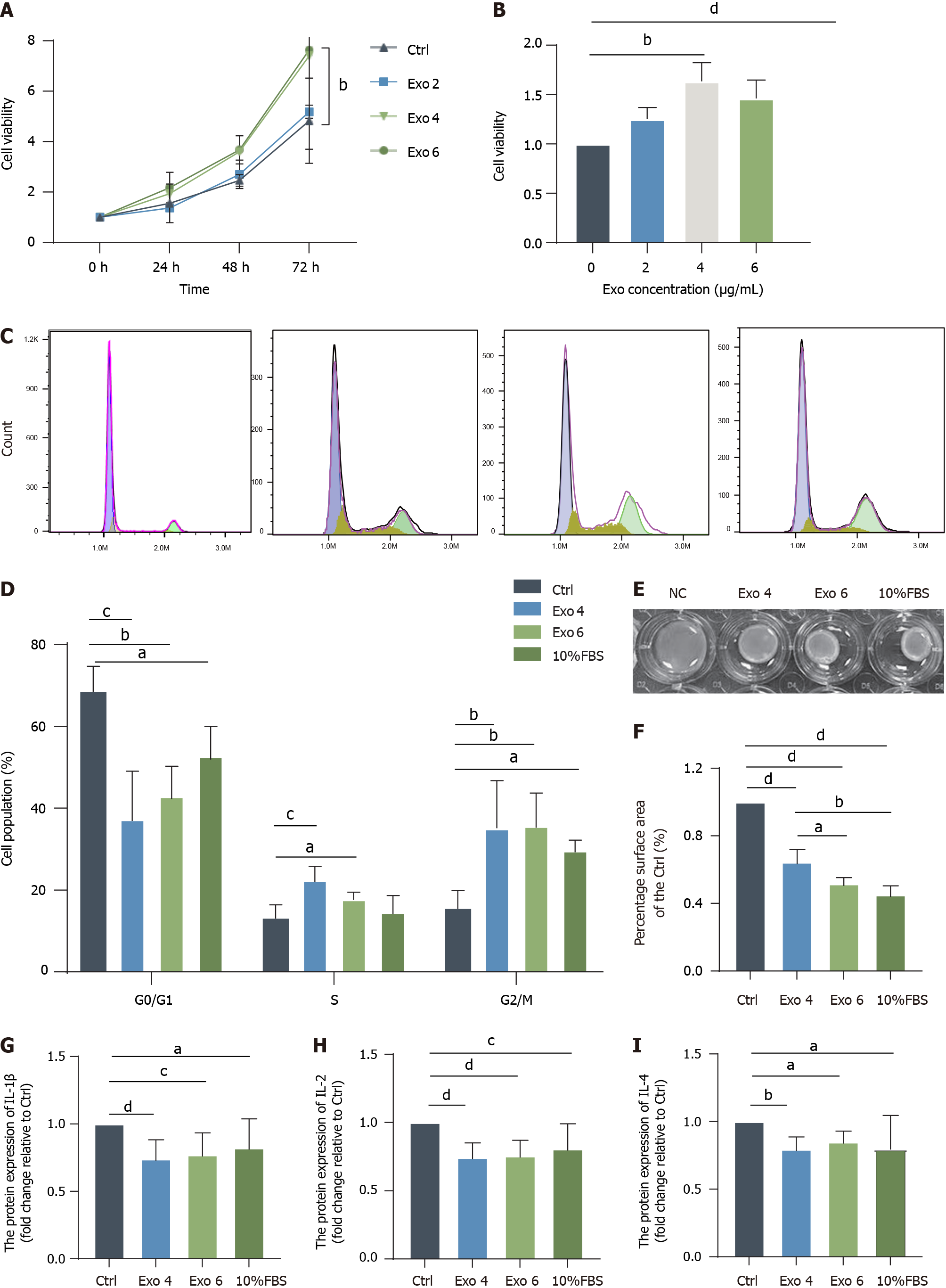
Figure 5 Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosome stimulated the growth and contractility of fibroblasts.
A: A Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay was used to detect the effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosome (hucMSC-Exo) on the viability of fibroblasts from 0 h to 72 h; B: Quantification of the CCK-8 results at 48 h; C and D: Flow cytometric analysis of the cell cycle distribution of fibroblasts exposed to hucMSC-Exo and quantification of the results at 48 h; E and F: Representative images and quantification of gel contraction following incubation with hucMSC-Exo (4 or 6 μg/mL) for 48 h. Gel contraction was measured as a percentage of the area of the control group; G-I: Culture supernatant was collected after fibroblasts from the 4 groups were treated for 48 h, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was conducted to determine the levels of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-2 and IL-4. The data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA (means ± SD). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001; dP < 0.0001. Exo: Exosome; IL: Interleukin; FBS: Fetal bovine serum.
- Citation: Xu LM, Yu XX, Zhang N, Chen YS. Exosomes from umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells promote the collagen production of fibroblasts from pelvic organ prolapse. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(6): 708-727
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i6/708.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.708