Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2024; 16(6): 708-727
Published online Jun 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.708
Published online Jun 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.708
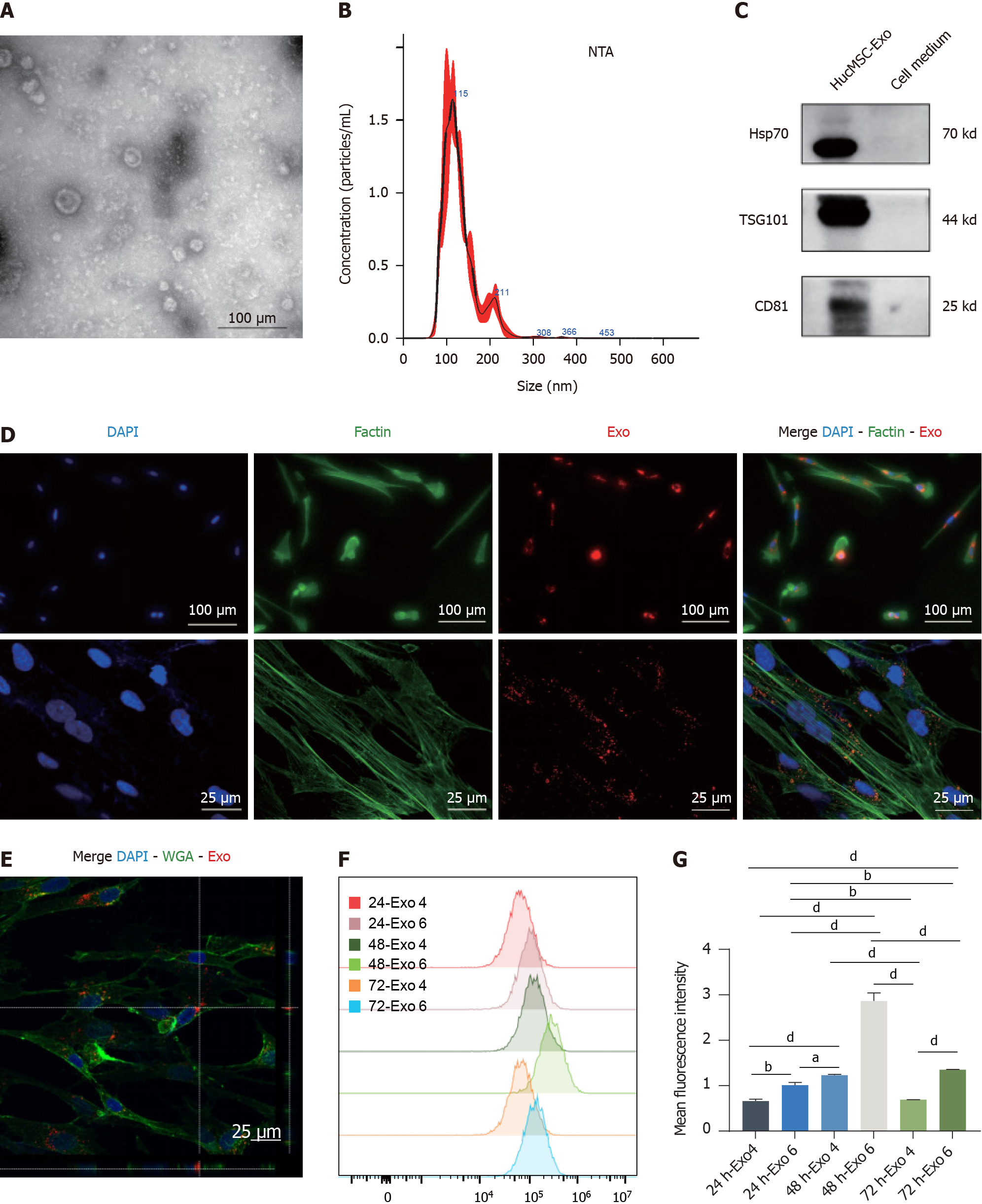
Figure 4 Identification and internalization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes.
A: TEM was utilized to obtain representative images of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosome (hucMSC-Exo) (scale bar: 200 μm); B: NTA of the size distribution and concentration of hucMSC-Exo; C: Western blot analysis for the detection of the hucMSC-Exo surface markers heat shock protein 70, TSG101, and CD81; D: Observation of PKH-26-hucMSC-Exo internalization by fibroblasts via both fluorescence microscopy and laser confocal microscopy; E: The 3D image of hucMSC-Exo internalized by fibroblasts; F and G: The median fluorescence intensity (F) and quantification (G) of hucMSC-Exo uptaken by fibroblasts with 4 μg/mL and 6 μg/mL after treatment for 24, 48, and 72 h via FCM. DAPI is blue, PKH26 is red, F-actin is green in D, Wheat germ agglutinin is green in E. Scale bars: 50 μm and 25 μm. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; dP < 0.0001. HSP: Heat shock protein; Exo: Exosome.
- Citation: Xu LM, Yu XX, Zhang N, Chen YS. Exosomes from umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells promote the collagen production of fibroblasts from pelvic organ prolapse. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(6): 708-727
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i6/708.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.708