Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2024; 16(6): 690-707
Published online Jun 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.690
Published online Jun 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.690
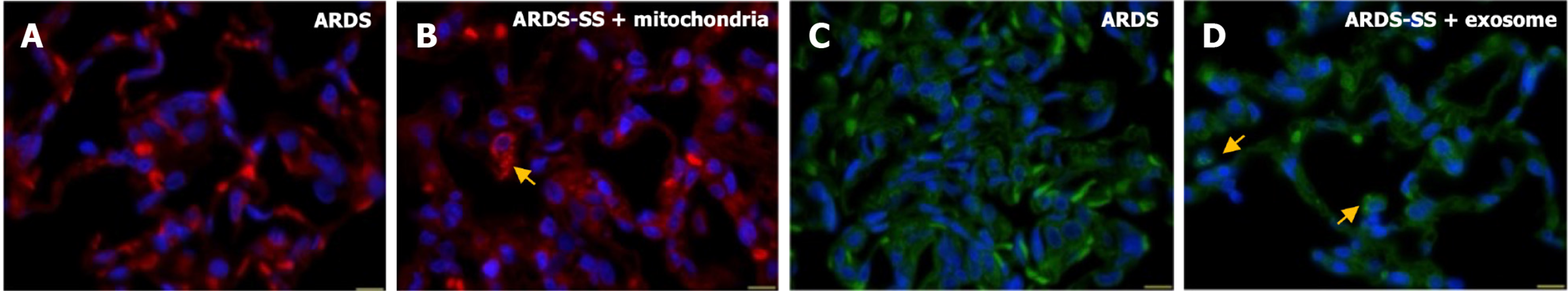
Figure 9 Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes-exogenous mitochondria were identified in the lung parenchyma of acute respiratory distress syndrome rat by day 5 after acute respiratory distress syndrome induction.
A and B: Illustrating the immuno
- Citation: Lin KC, Fang WF, Yeh JN, Chiang JY, Chiang HJ, Shao PL, Sung PH, Yip HK. Outcomes of combined mitochondria and mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosome therapy in rat acute respiratory distress syndrome and sepsis. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(6): 690-707
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i6/690.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.690