Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2024; 16(6): 690-707
Published online Jun 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.690
Published online Jun 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.690
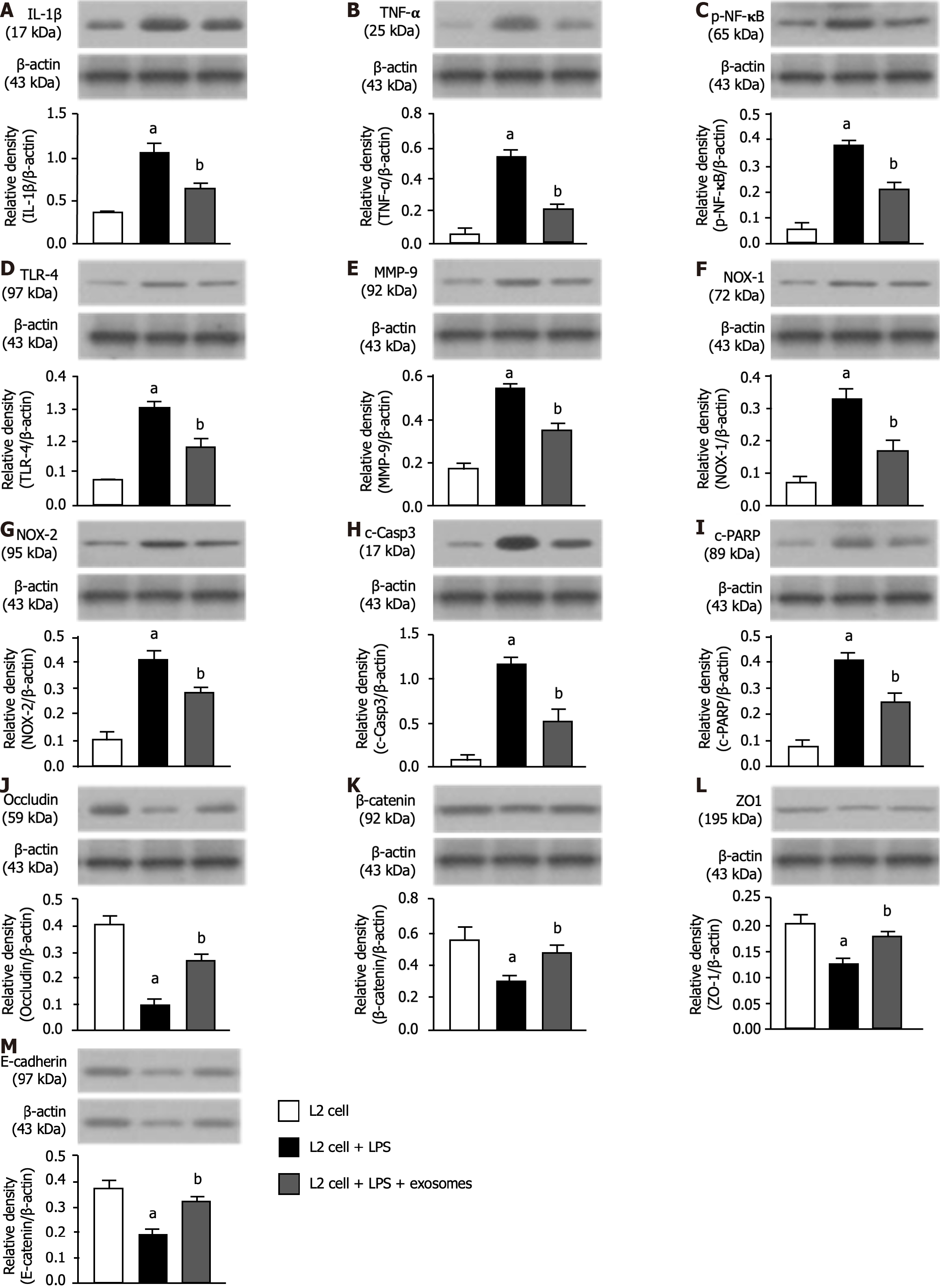
Figure 4 Exosomes therapy effectively reduced inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis and preserved the lung epithelial cell junctions.
A: Protein expression of interleukin-1β; B: Protein expression of tumor necrosis factor-α; C: Protein expression of nuclear factor-κB; D: Protein expression of toll-like receptor-4; E: Protein expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9; F: Protein expression of NOX-1; G: Protein expression of NOX-2; H: Protein expression of cleaved caspase 3; I: Protein expression of cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; J: Protein expression of occludin; K: Protein expression of β-catenin; L: Protein expression of zonula occludens-1; M: Protein expression of E-cadherin. All statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni multiple comparison post hoc test (n = 3 for each group). Control vs other groups with different letters, aP < 0.001, bP < 0.01. B1: L2 cells only; B2: L2 cells + lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (1.0 μg/mL); B3: L2 cells + LPS (1.0 μg/mL) + exosomes (10 μg). IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; NF-κB: Nuclear factor NF-κB; TLR: Toll-like receptor; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; c-Casp3: Cleaved caspase 3; ZO-1: Zonula occludens-1; PARP: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; LPS: lipopolysaccharide.
- Citation: Lin KC, Fang WF, Yeh JN, Chiang JY, Chiang HJ, Shao PL, Sung PH, Yip HK. Outcomes of combined mitochondria and mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosome therapy in rat acute respiratory distress syndrome and sepsis. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(6): 690-707
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i6/690.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.690