Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2024; 16(6): 670-689
Published online Jun 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.670
Published online Jun 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.670
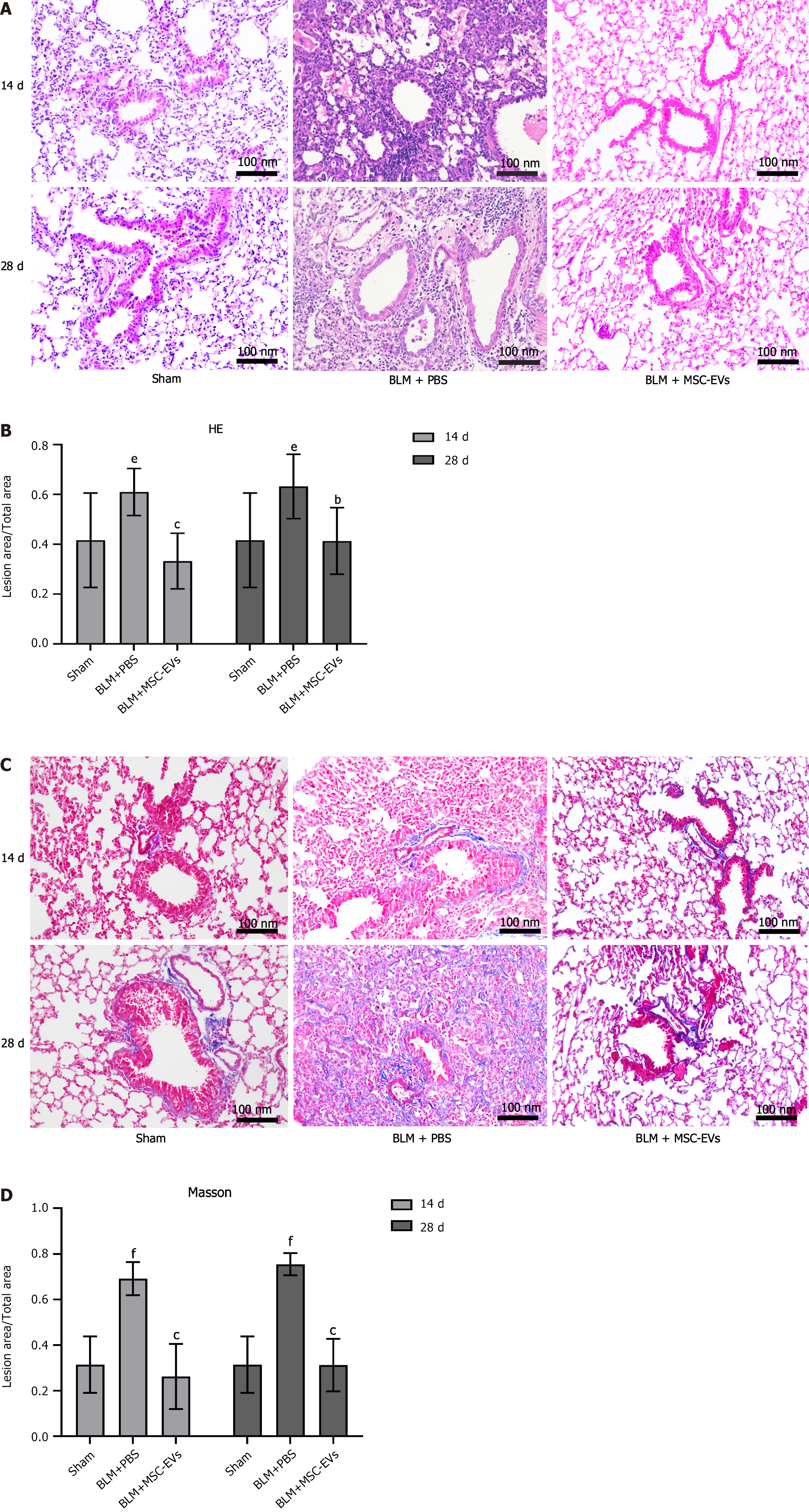
Figure 2 Bleomycin can induce pulmonary fibrosis and inflammatory infiltration in mice.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining of lung tissue of mice in each group on days 14 and 28 after administration. Inflammatory cells are basophilic (blue-purple granules), and their number represents the severity of inflammation in the lung tissue of mice; B: The quantitative statistical analysis of HE staining on days 14 and 28 among the three groups. The ordinate represents the percentage of the inflammatory area in the total area, and the abscissa represents the grouping. In the bleomycin group, there were significant inflammatory reactions on day 14 (eP < 0.01 vs sham group) and day 28 (eP < 0.01 vs sham group). After exosome treatment, the inflammatory reactions were significantly improved on day 14 (cP < 0.001) and day 28 (bP < 0.01); C: Masson staining of lung tissue of mice in each group on days 14 and 28 after administration. Collagen fibers appear blue, and their number represents the severity of collagen deposition in the lungs of mice; D: The quantitative statistical analysis of Masson staining. The ordinate represents the percentage of collagen fiber deposition area in the total area, and the abscissa represents the grouping. In the bleomycin group, significant collagen deposition occurred on day 14 (fP < 0.001 vs sham group) and day 28 (fP < 0.001 vs sham group). After exosome treatment, the collagen deposition decreased on day 14 (cP < 0.001) and day 28 (cP < 0.001). MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; EV: Extracellular vesicle; BLM: Bleomycin; PBS: Phosphate buffered saline.
- Citation: Gao Y, Liu MF, Li Y, Liu X, Cao YJ, Long QF, Yu J, Li JY. Mesenchymal stem cells-extracellular vesicles alleviate pulmonary fibrosis by regulating immunomodulators. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(6): 670-689
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i6/670.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i6.670