Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2024; 16(5): 525-537
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.525
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.525
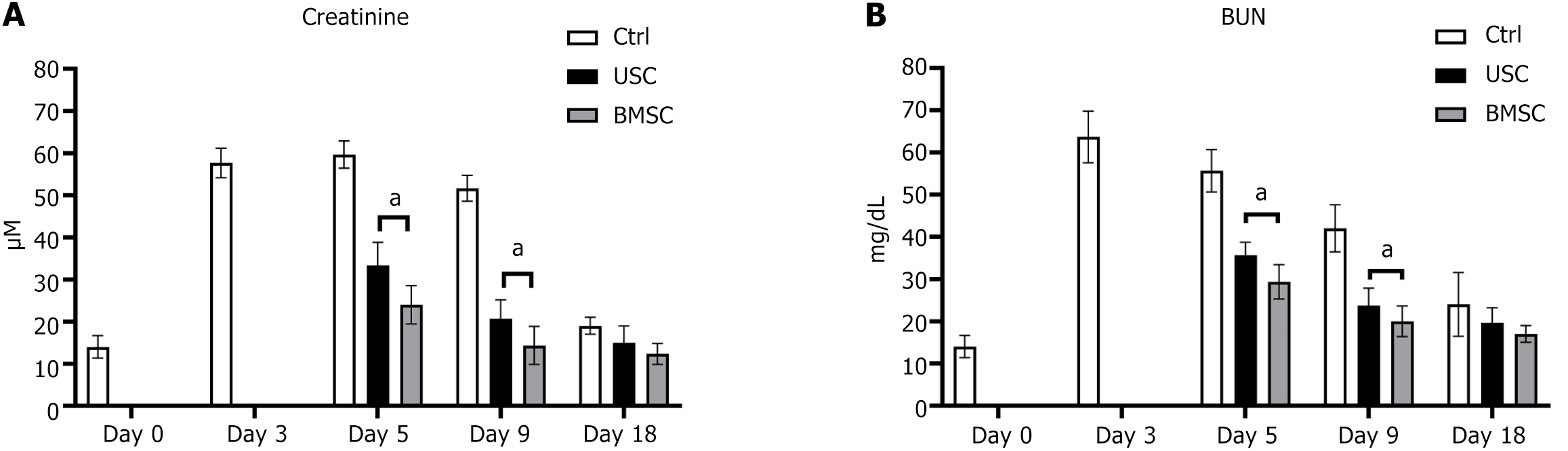
Figure 5 Assessment of renal function.
A and B: The changes in renal function were assessed by measuring creatinine levels (A) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels (B). After glycerol injection, the creatinine levels increased starting on day three. However, in mice administered urine-derived stem cells or bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, the creatinine levels decreased to near baseline levels within 48 h post-injection and remained stable for the duration of the experiment (A). A similar trend was observed when measuring BUN levels (B). To determine the statistical significance of these results, an analysis of variance was performed. aP < 0.05, the comparison between stem cell-treated and untreated groups showed statistical significance. BUN: Blood urea nitrogen; USC: Urine-derived stem cell; BMSC: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell.
- Citation: Li F, Zhao B, Zhang L, Chen GQ, Zhu L, Feng XL, Gong MJ, Hu CC, Zhang YY, Li M, Liu YQ. Therapeutic potential of urine-derived stem cells in renal regeneration following acute kidney injury: A comparative analysis with mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(5): 525-537
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i5/525.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.525