Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2024; 16(5): 512-524
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.512
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.512
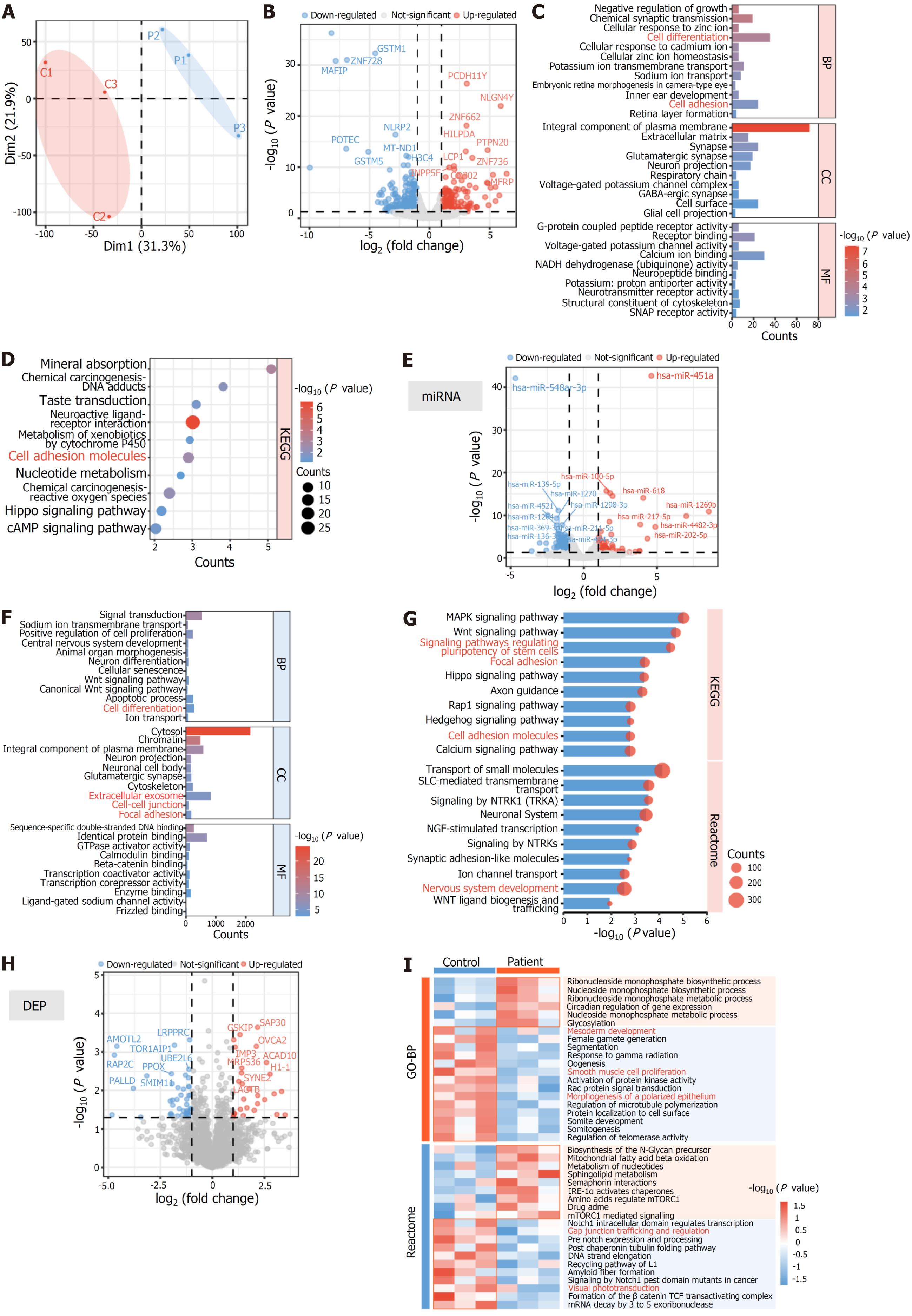
Figure 4 Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses identifying defects of cell adhesion and differentiation in patient-derived human induced pluripotent stem cells.
A: Principal component analysis of mRNA expression; B: Differentially expressed mRNAs between patient human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and control iPSCs; C: Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis for differentially expressed genes; D: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis for differentially expressed genes; E: Differentially expressed microRNAs (miRNAs) between patient iPSCs and control iPSCs; F: GO enrichment analysis for differentially expressed miRNA target genes; G: KEGG and Reactome enrichment analyses for differentially expressed miRNA target genes; H: Differentially expressed proteins between patient iPSCs and control iPSCs; I: GO and Reactome enrichment analyses for differentially expressed proteins. GO: Gene Ontology; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; BP: Biological progress; CC: Cellular component; MF: Molecular function; miRNA: MicroRNA; DEP: Differentially expressed protein.
- Citation: Zhang H, Wu LZ, Liu ZY, Jin ZB. Patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells with a MERTK mutation exhibit cell junction abnormalities and aberrant cellular differentiation potential. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(5): 512-524
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i5/512.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.512