Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2024; 16(5): 499-511
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.499
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.499
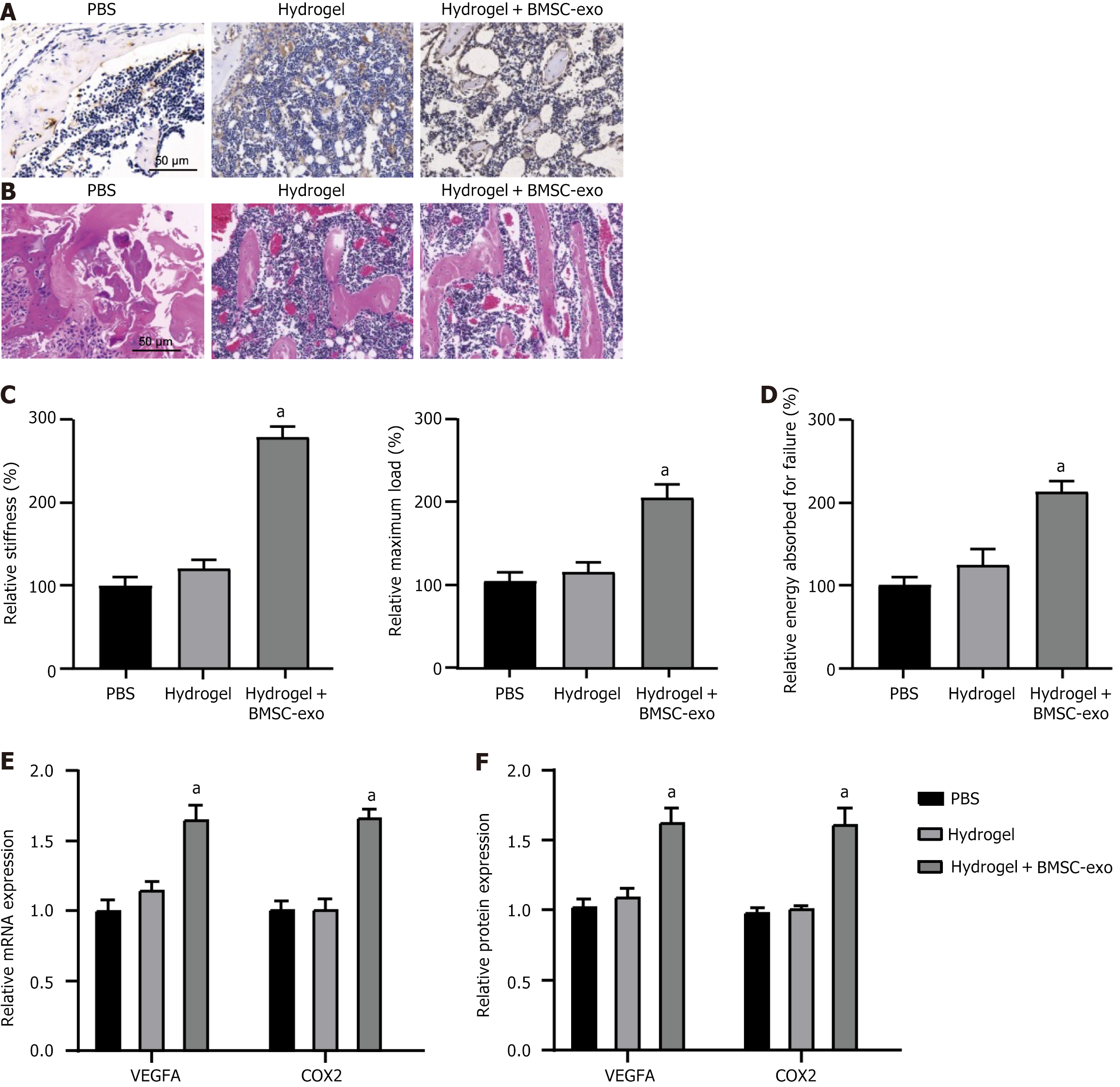
Figure 6 Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome hydrogel promoted fracture healing and angiogenesis in vivo.
A: Alcian blue and orange G staining of regenerated bone sections treated by hydrogels with or without bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell (BMSC)-derived exosome (BMSC-exo) on week 2 and week 4 after fracture; B: Hematoxylin-eosin staining of regenerated bone tissues; C and D: Maximum load, stiffness, and energy absorbed for failure or repaired bone; E and F: mRNA and protein expression of angiogenesis markers (vascular endothelial growth factor A and cyclooxygenase-2) in fracture healing model treated by hydrogels with or without BMSC-exo. n = 6, aP < 0.05. VEGFA: Vascular endothelial growth factor A; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; BMSC-exo: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome; PBS: Phosphate buffered saline.
- Citation: Zhang S, Lu C, Zheng S, Hong G. Hydrogel loaded with bone marrow stromal cell-derived exosomes promotes bone regeneration by inhibiting inflammatory responses and angiogenesis. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(5): 499-511
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i5/499.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.499