Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2024; 16(5): 499-511
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.499
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.499
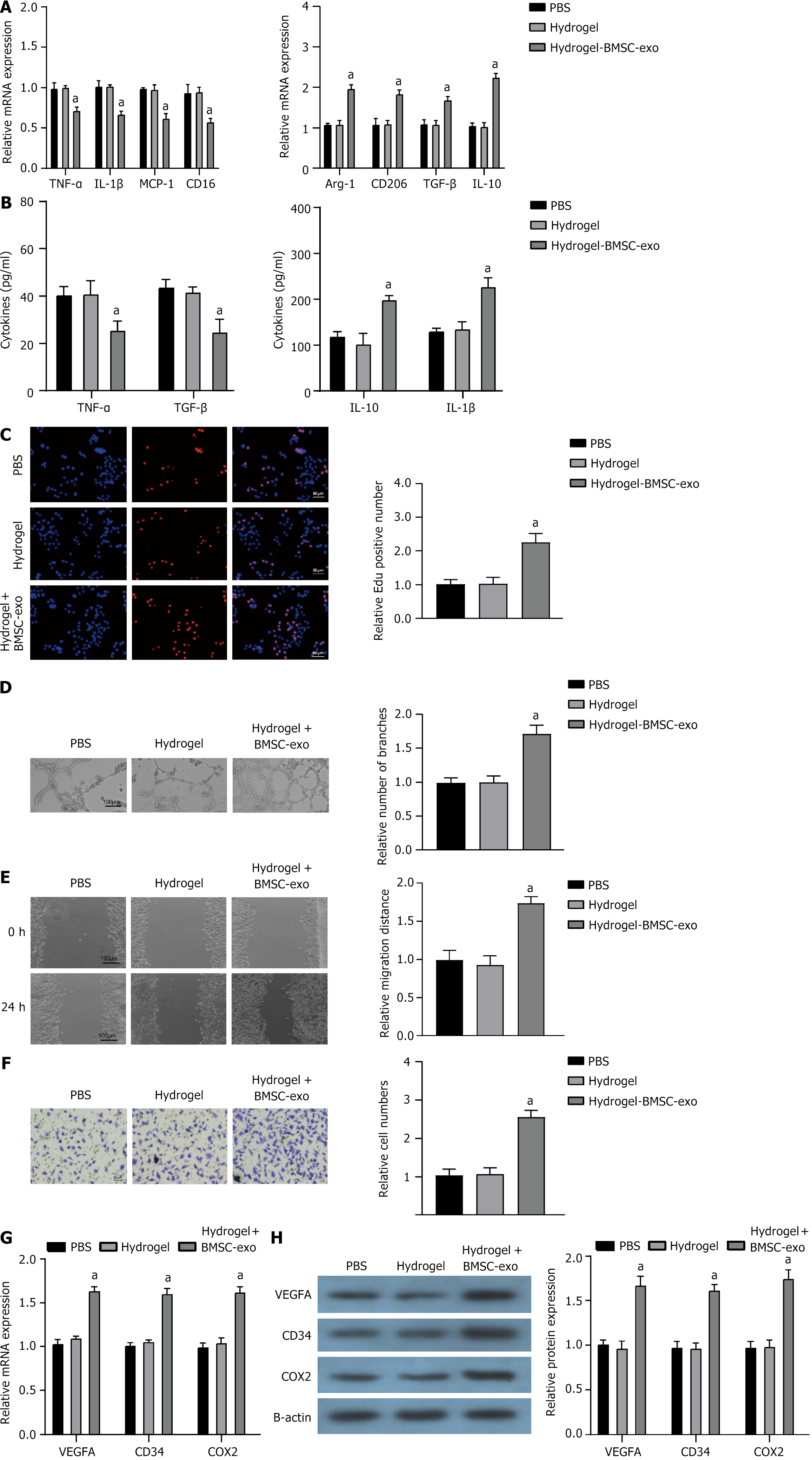
Figure 5 Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome hydrogels effectively suppressed the inflammatory response of macrophages while facilitating angiogenesis.
A: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction assessment of mRNA expression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, CD16, arginase-1, CD206, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, and IL-10 in RAW264.7 cells cultured on hydrogels with or without bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell (BMSC)-derived exosome (BMSC-exo) for 24 h; B: Expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, TGF-β, and IL-10 cytokines was assessed in RAW264.7 macrophages across different experimental groups; C: Cells proliferation of mouse osteoblast progenitor cells (mOPCSs) co-cultured with human umbilical vein endothelial cell in different groups by fluorescence microscopy; D: Tube formation assay of mOPCs in different groups. Scale bar: 50 μm; E and F: Scratch wound healing assay and Transwell migration assay of mOPCSs in different groups. The hydrogel + BMSC-exo group demonstrated enhanced migration, Scale bar: 50 μm; G and H: mRNA and protein expression of angiogenesis markers (vascular endothelial growth factor A, CD34, and cyclooxygenase-2) in mOPCSs in different groups. aP < 0.05. TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; Arg-1: Arginase-1; TGF: Transforming growth factor; VEGFA: Vascular endothelial growth factor A; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; BMSC-exo: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome; PBS: Phosphate buffered saline.
- Citation: Zhang S, Lu C, Zheng S, Hong G. Hydrogel loaded with bone marrow stromal cell-derived exosomes promotes bone regeneration by inhibiting inflammatory responses and angiogenesis. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(5): 499-511
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i5/499.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.499