Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2024; 16(5): 499-511
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.499
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.499
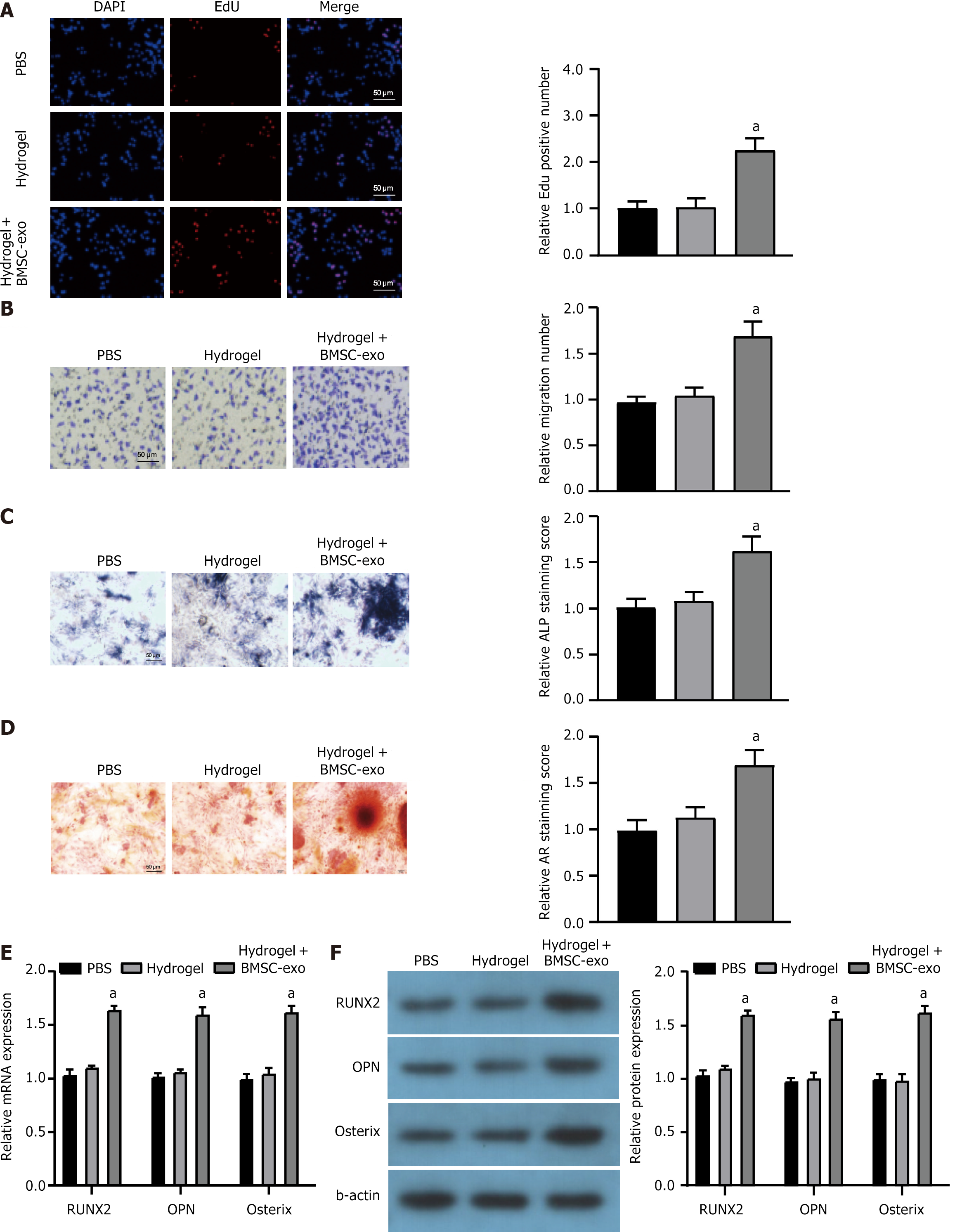
Figure 4 Fabrication and efficacy of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome-treated hydrogel.
A: Cells proliferation of mouse osteoblast progenitor cells (mOPCSs) with different treatments by fluorescence microscopy; B: mOPCSs with hydrogel or bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell (BMSC)-derived exosome (BMSC-exo)-treated hydrogel stained by crystal violet in Transwell assays. Hydrogel + BMSC-exo enhanced cell migration, Scale bar: 50 μm; C: Alkaline phosphatase staining of mOPCSs treated with hydrogel or hydrogel + BMSC-exo for one week. Scale bar: 50 μm; D: Alizarin red staining of mOPCSs with different treatments after osteogenic induction for two weeks. Scale bar: 50 μm; E and F: mRNA and protein expression of genes associated with osteogenesis (Runx2, OPN, and Osterix) in mOPCSs with different treatments. aP < 0.05. BMSC-exo: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome; PBS: Phosphate buffered saline; DAPI: 4’,6’-diaminido-2-phenylindole; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase.
- Citation: Zhang S, Lu C, Zheng S, Hong G. Hydrogel loaded with bone marrow stromal cell-derived exosomes promotes bone regeneration by inhibiting inflammatory responses and angiogenesis. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(5): 499-511
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i5/499.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.499