Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2024; 16(5): 486-498
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.486
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.486
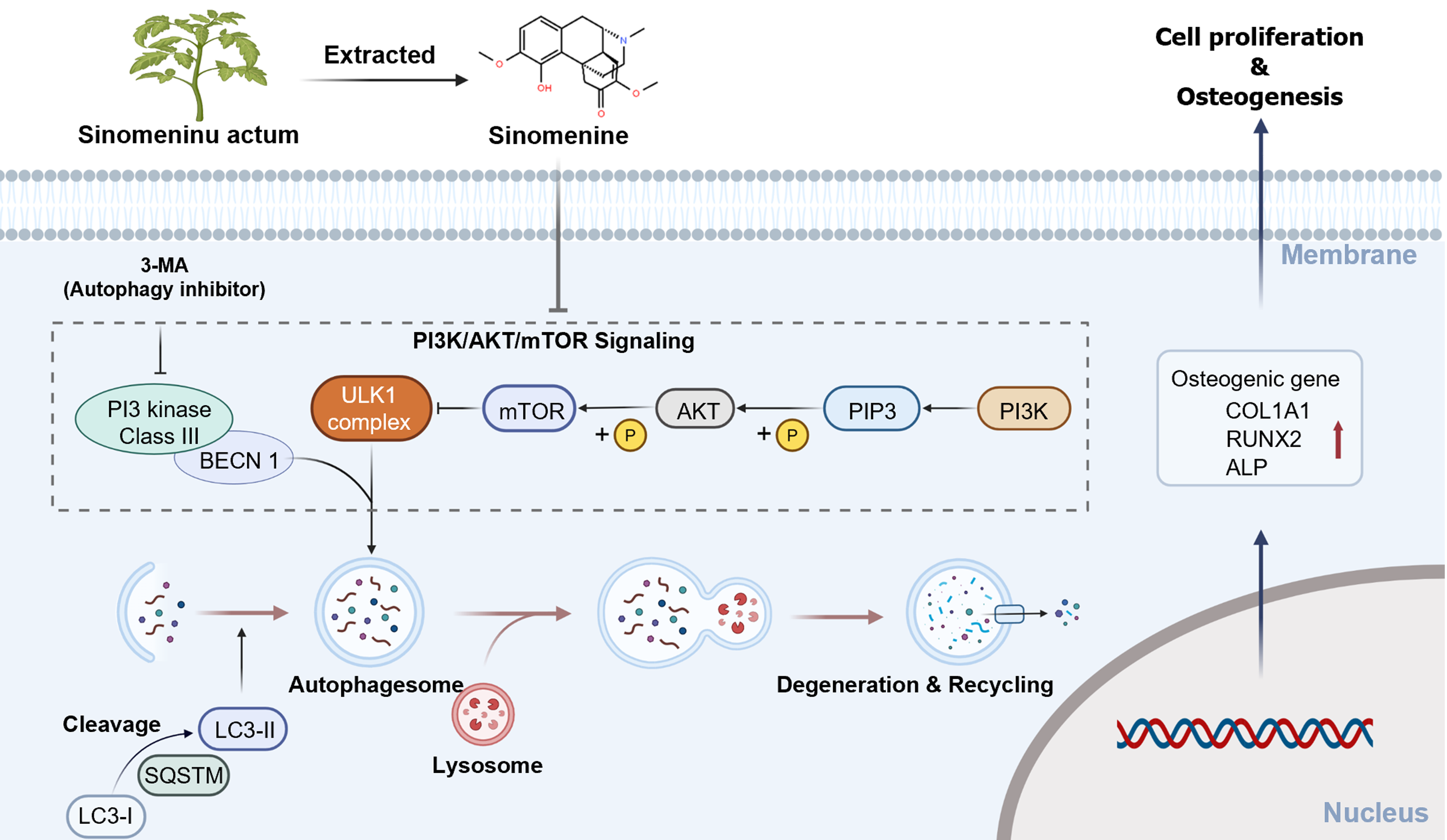
Figure 5 Schematic illustration showing the mechanism by which sinomenine promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells through modulation of autophagy.
Sinomenine decreased the levels of AKT and mammalian target of the rapamycin (mTOR) phosphorylation in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, and reduced mTOR activation lifted the inhibition of downstream autophagy and increased cellular autophagosomes, which increased the viability and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells. 3-MA: 3-methyladenine; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; mTOR: Mammalian target of the rapamycin.
- Citation: Xiao HX, Yu L, Xia Y, Chen K, Li WM, Ge GR, Zhang W, Zhang Q, Zhang HT, Geng DC. Sinomenine increases osteogenesis in mice with ovariectomy-induced bone loss by modulating autophagy. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(5): 486-498
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i5/486.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.486