Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2024; 16(5): 486-498
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.486
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.486
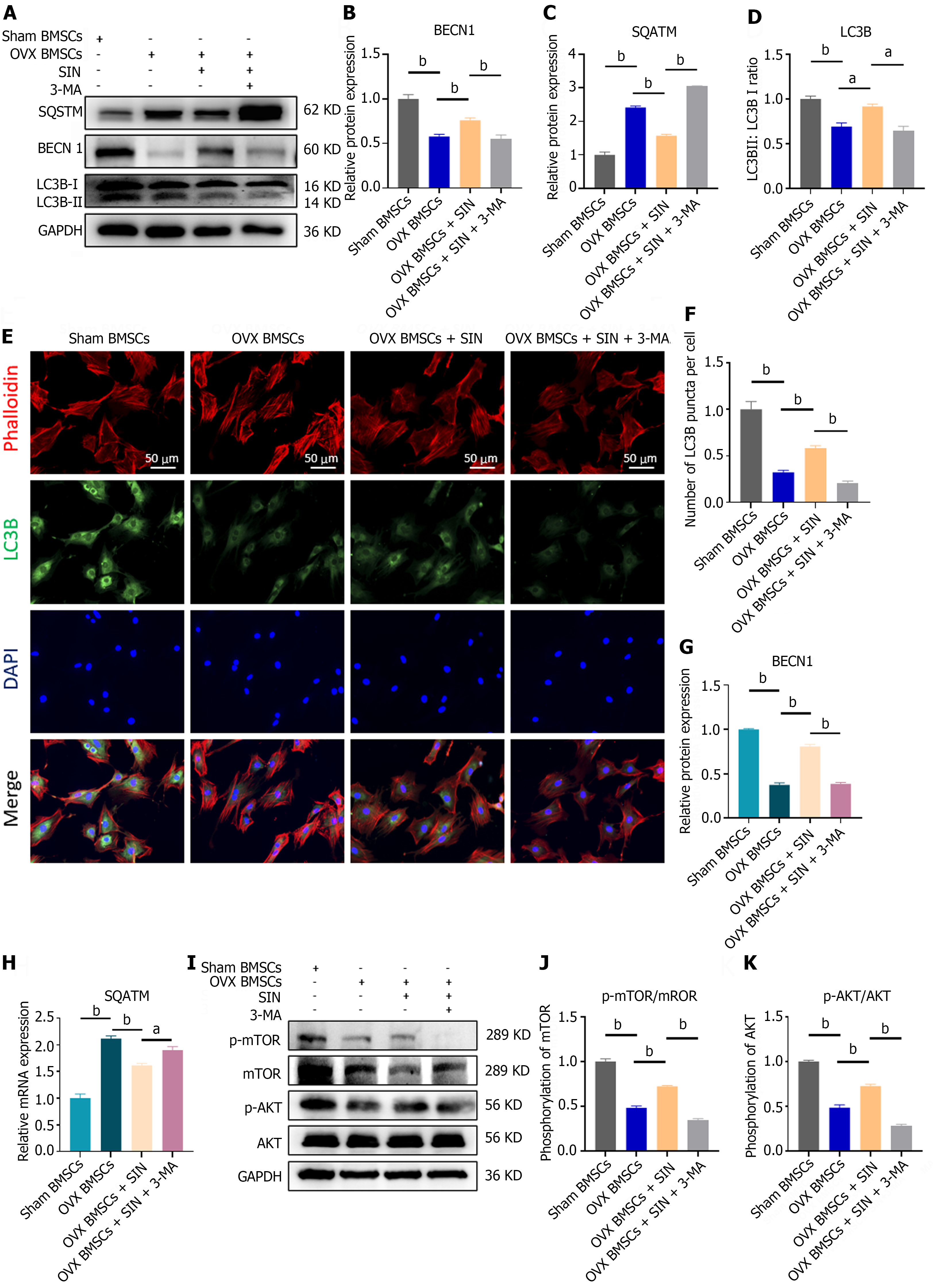
Figure 4 Sinomenine upregulates autophagy in bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/mammalian target of the rapamycin pathway.
A-D: Protein levels of SQSTM, BECN1 and LC3B II/LC3B I after sinomenine (SIN) treatment (12 h); E and F: Quantitative analysis of the average fluorescence intensity of LC3B; G and H: BECN1 and SQSTM mRNA levels after SIN and 3-methyladenine (3-MA) treatment (12 h); I-K: Protein levels of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and AKT and mammalian target of the rapamycin phosphorylation levels after SIN and 3-MA treatment (12 h). n = 3 per group. Values are shown as the means ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, all data were normalized relative to the sham bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cell group. OVX: Ovariectomized; SIN: Sinomenine; 3-MA: 3-methyladenine; BMSC: Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cell; mTOR: Mammalian target of the rapamycin.
- Citation: Xiao HX, Yu L, Xia Y, Chen K, Li WM, Ge GR, Zhang W, Zhang Q, Zhang HT, Geng DC. Sinomenine increases osteogenesis in mice with ovariectomy-induced bone loss by modulating autophagy. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(5): 486-498
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i5/486.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.486