Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2024; 16(5): 486-498
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.486
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.486
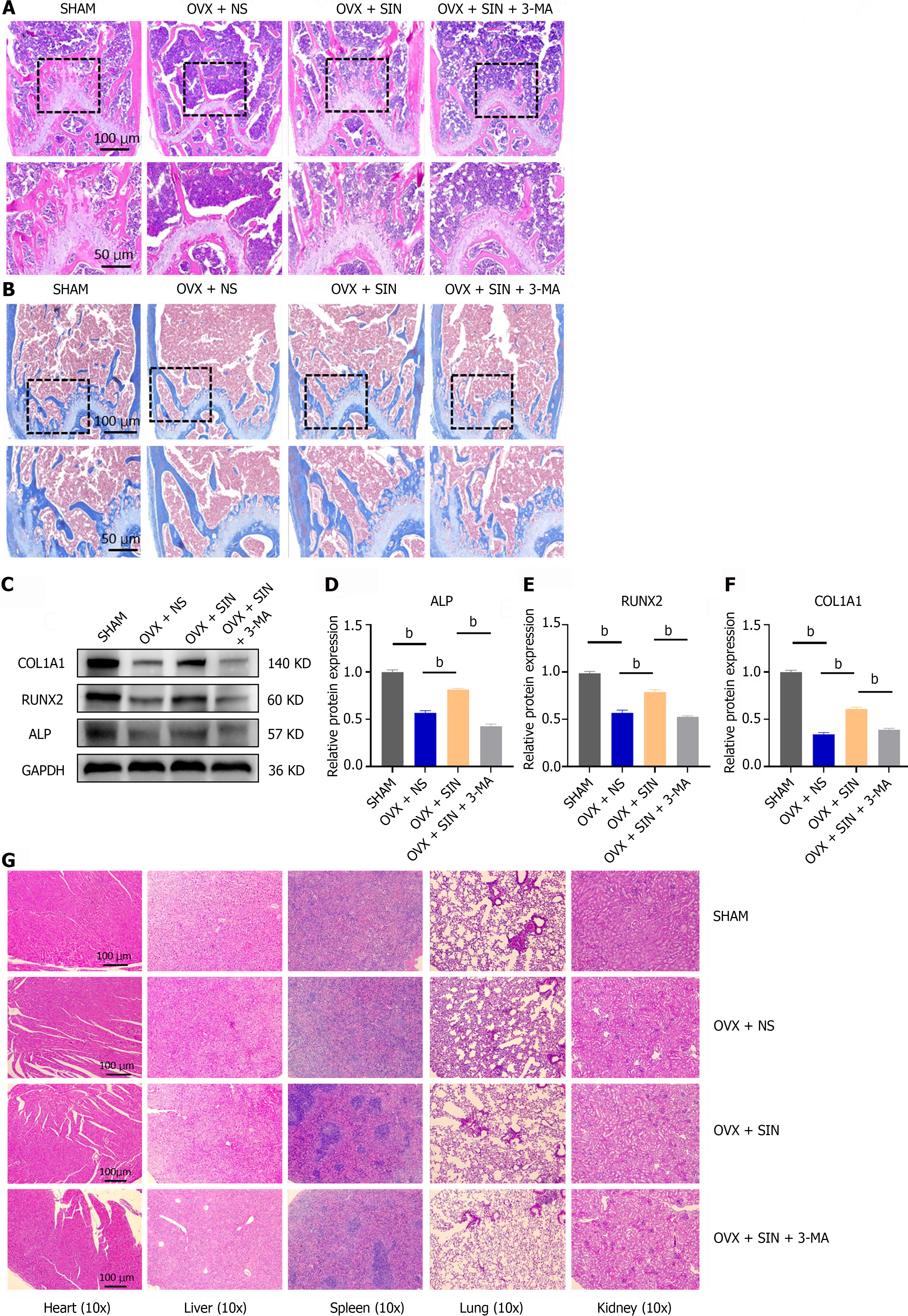
Figure 2 Morphology, quantitative protein assay of femur and visceral toxicity assays.
A: Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining images of trabecular bone under the distal femur growth plate from the sham group, ovariectomized (OVX) + NS group, OVX + sinomenine (SIN) group, and OVX + SIN + 3-methyladenine (3-MA) group; B: Representative Masson staining images of trabecular bone under the distal femur growth plate from each group; C-F: Protein levels of ALP, RUNX2 and COL1A1 in mouse bone tissues; G: Effects of SIN and 3-MA on organ tissues. H&E staining was performed on heart, lung, liver, spleen and kidney sections. No changes in organ structure were observed, indicating that the administration of SIN and 3-MA had no harmful effects on organ tissues in this study. Three fields were randomly selected for each sample, and 5 biologically independent mouse samples were used in each group. n = 3 per group. Values are shown as the mean ± SD. bP < 0.01, all data were normalized relative to the sham group. OVX: Ovariectomized; SIN: Sinomenine; 3-MA: 3-methyladenine.
- Citation: Xiao HX, Yu L, Xia Y, Chen K, Li WM, Ge GR, Zhang W, Zhang Q, Zhang HT, Geng DC. Sinomenine increases osteogenesis in mice with ovariectomy-induced bone loss by modulating autophagy. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(5): 486-498
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i5/486.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i5.486