Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2024; 16(4): 434-443
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.434
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.434
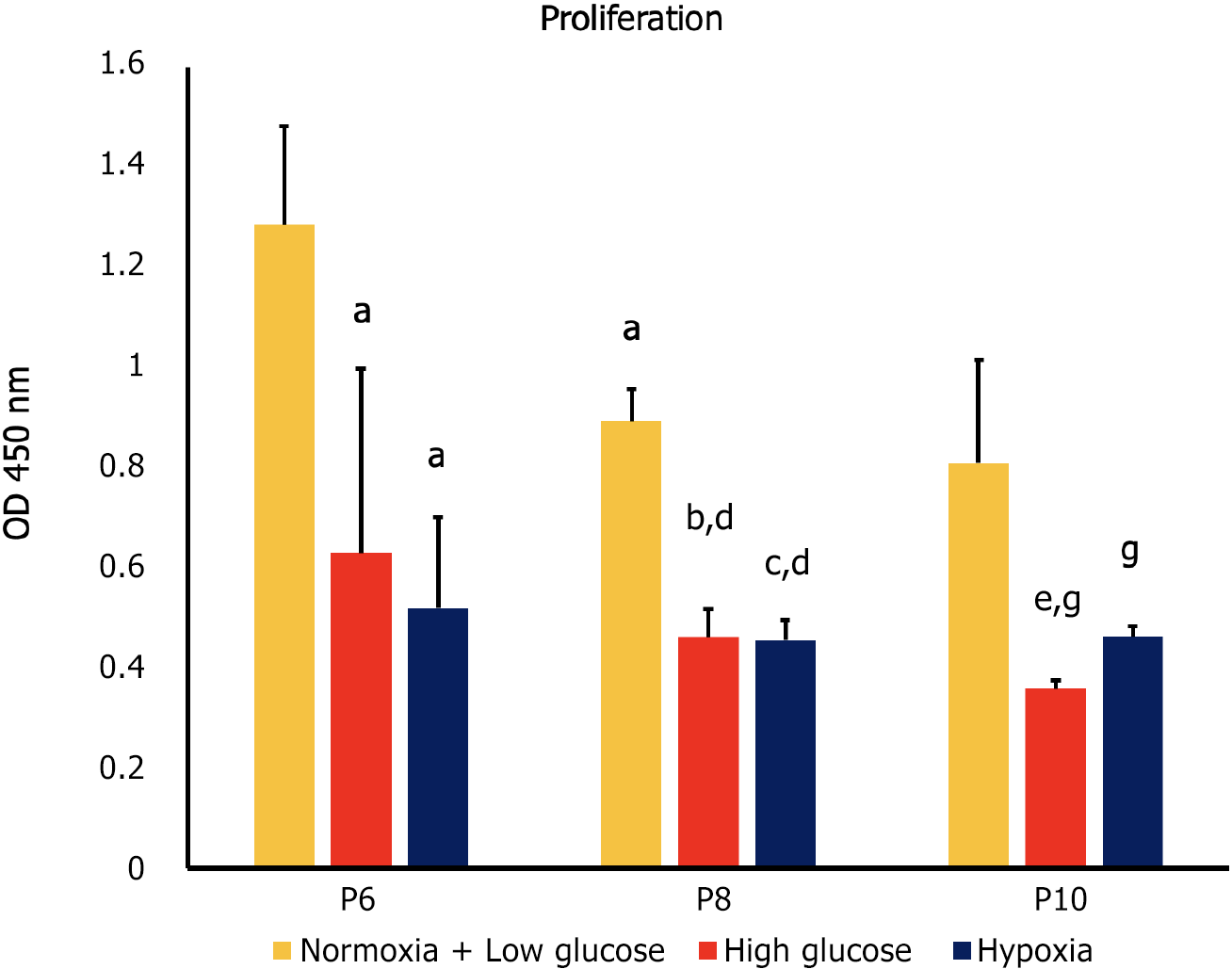
Figure 1 Proliferation of human adipose-tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells at passages 6, 8 and 10 under conditions of normoxia + low glucose (control), high glucose and hypoxia, as measured by WST-1.
High glucose and hypoxia were associated with a significant decrease in proliferation of human adipose-tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) compared to control cells at each of the studied passages (P6, P8, and P10). At P8, proliferation was significantly decreased in all MSC groups compared to their counterparts at P6. At P10 only MSCs cultured in high glucose exhibited a significant decrease in proliferation compared to the same condition at P8. aP < 0.05 vs passages 6 (P6) normoxia + low glucose; bP < 0.05 vs P6 high glucose; cP < 0.05 vs P6 hypoxia; dP < 0.05 vs P8 normoxia + low glucose; eP < 0.05 compared to P8 high glucose; gP < 0.05 compared to P10 normoxia + low glucose. P6: Passage 6; P8: Passage 8; P10: Passage 10.
- Citation: Almahasneh F, Abu-El-Rub E, Khasawneh RR, Almazari R. Effects of high glucose and severe hypoxia on the biological behavior of mesenchymal stem cells at various passages. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(4): 434-443
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i4/434.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.434