Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2024; 16(4): 410-433
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.410
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.410
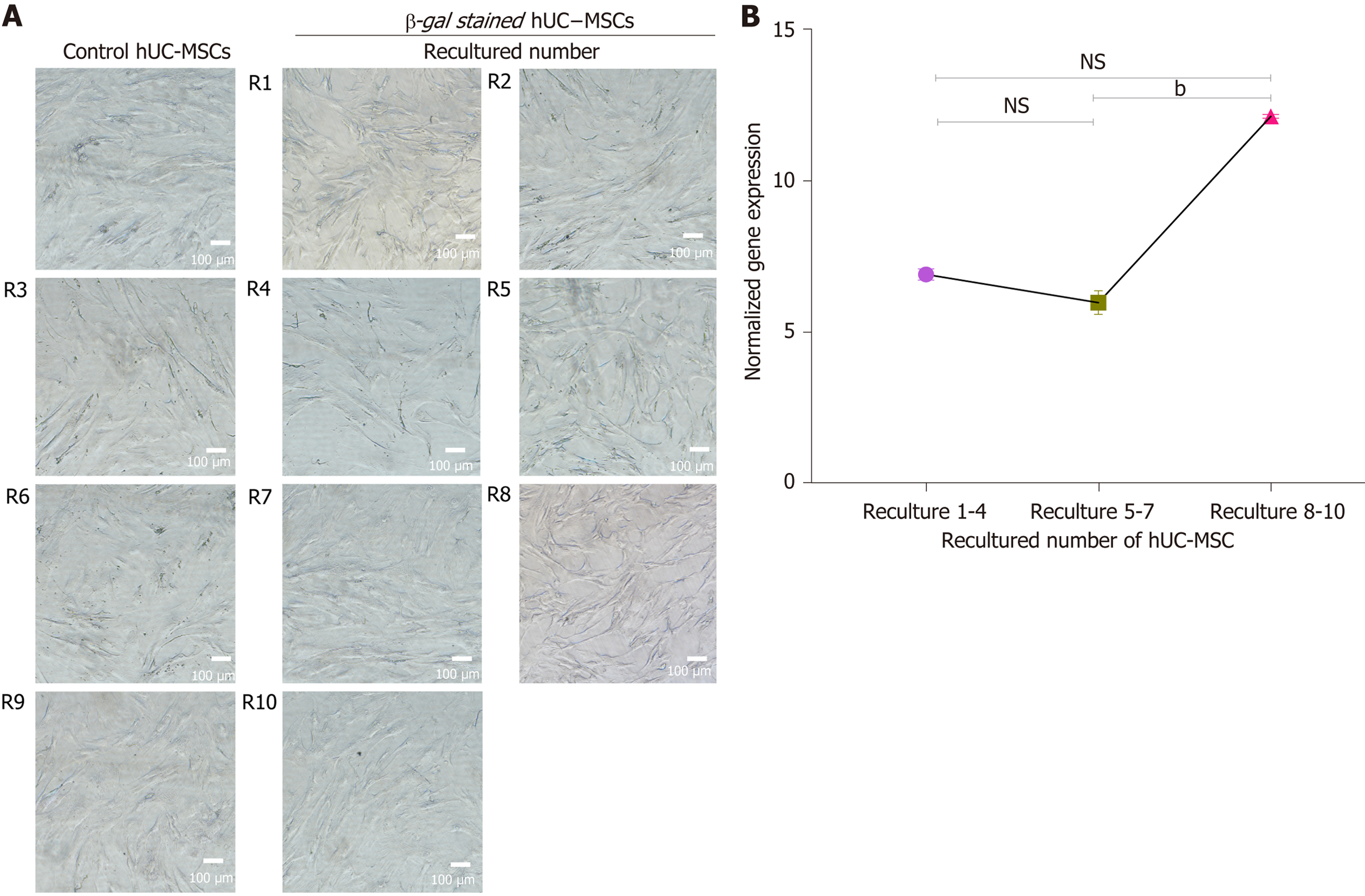
Figure 12 Cell senescence analysis.
A: The effect of recultured human umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) on cellular senescence: The β-galactosidase senescence staining was observed under bright field microscope. The results showed that none of the cells were stained blue, at primary isolated recultured hUC-MSCs isolated (R1-R10), indicating no signal of senescence; B: The graphical representation of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) expression in recultured hUC-MSCs: To evaluate the normalized telomerase activity quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was performed in triplicate at passages 1-6. The X-axis represents the MSCs derived from recultured hUC at three recultured range and Y-axis represents hTERT expression normalized to housekeeping gene hydroxymethyl-bilane synthase. The hTERT expression at recultured 1-4 and 5-7 showed no significant difference. However, a significant increase in hTERT activity at recultured 8-10 was observed. Values are presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. NS: No significance, bP < 0.01. hUC: Human umbilical cord; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell.
- Citation: Rajput SN, Naeem BK, Ali A, Salim A, Khan I. Expansion of human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(4): 410-433
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i4/410.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.410