Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2024; 16(4): 410-433
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.410
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.410
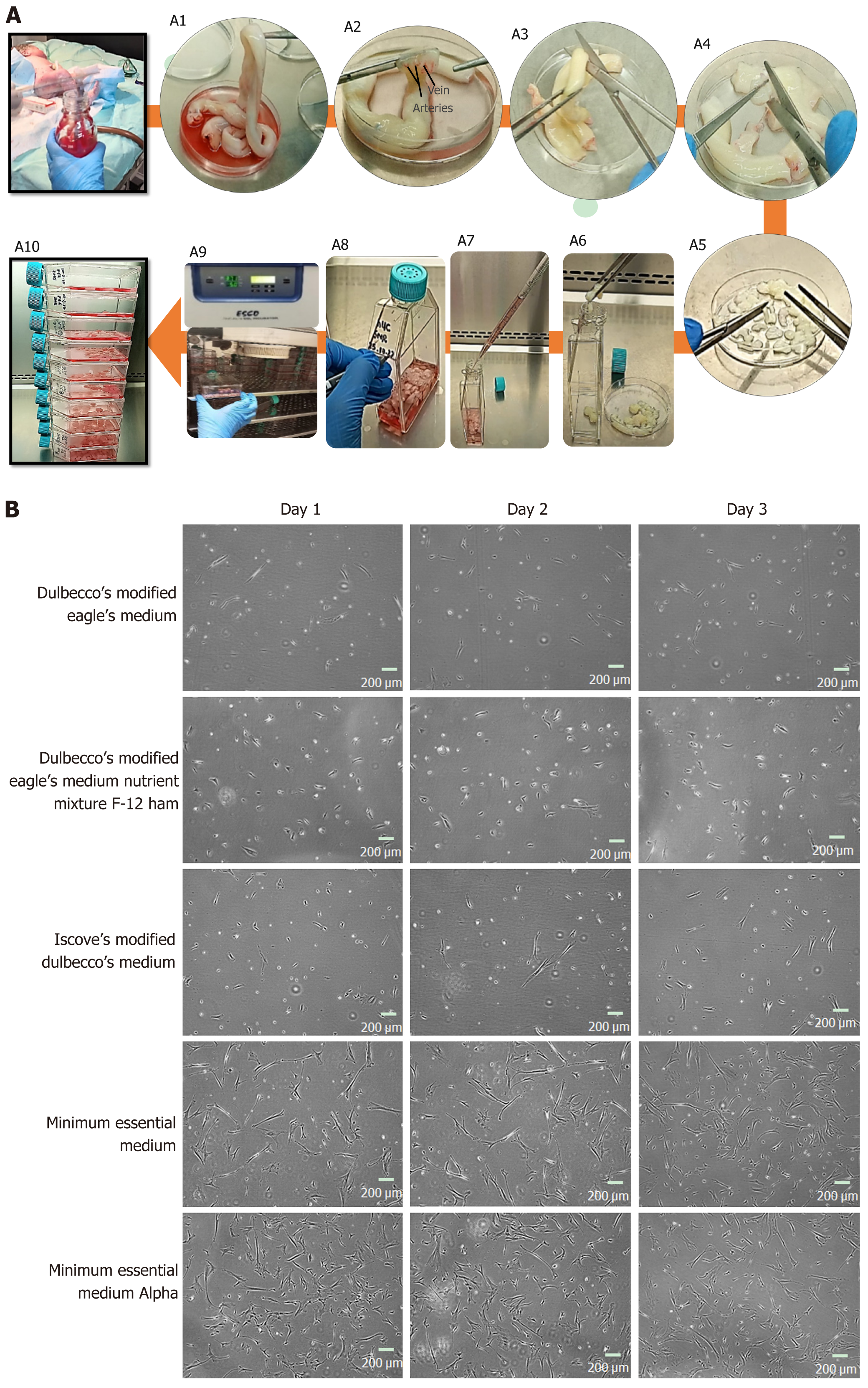
Figure 1 Human umbilical cord processing.
A: Representative images of human umbilical cord (hUC) collection, and culture. A1: The hUC manually collected and processed aseptically; A2: The collected cord samples were washed 5 to 6 times in 1× phosphate buffered saline, the embedded connective tissue of hUC consists of one vein and two arteries; A3: The cord samples were cut horizontally into roughly 5 cm sections; A4: An incision was made vertically to expose arteries and vein of hUC; A5: Cord sample were diced approximately into 3 mm × 3 mm pieces; A6: Cord pieces were transferred into T-75 flasks; A7: Complete minimal essential medium alpha (MEM α) was added 8-10 mL; A8: Flask was marked with respective hUC donor number; A9: The flasks were incubated undisturbed for up to 7 d at 37 °C supplied with 5% CO2; A10: Fresh medium was supplied without disturbing attached explant; B: Representative images of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) cultured in different mediums; sub-culture MSCs on different cultural mediums for 3 d, morphologically observed showed rapid adherent growth, and proliferation in MEM α.
- Citation: Rajput SN, Naeem BK, Ali A, Salim A, Khan I. Expansion of human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(4): 410-433
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i4/410.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.410