Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2024; 16(4): 389-409
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.389
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.389
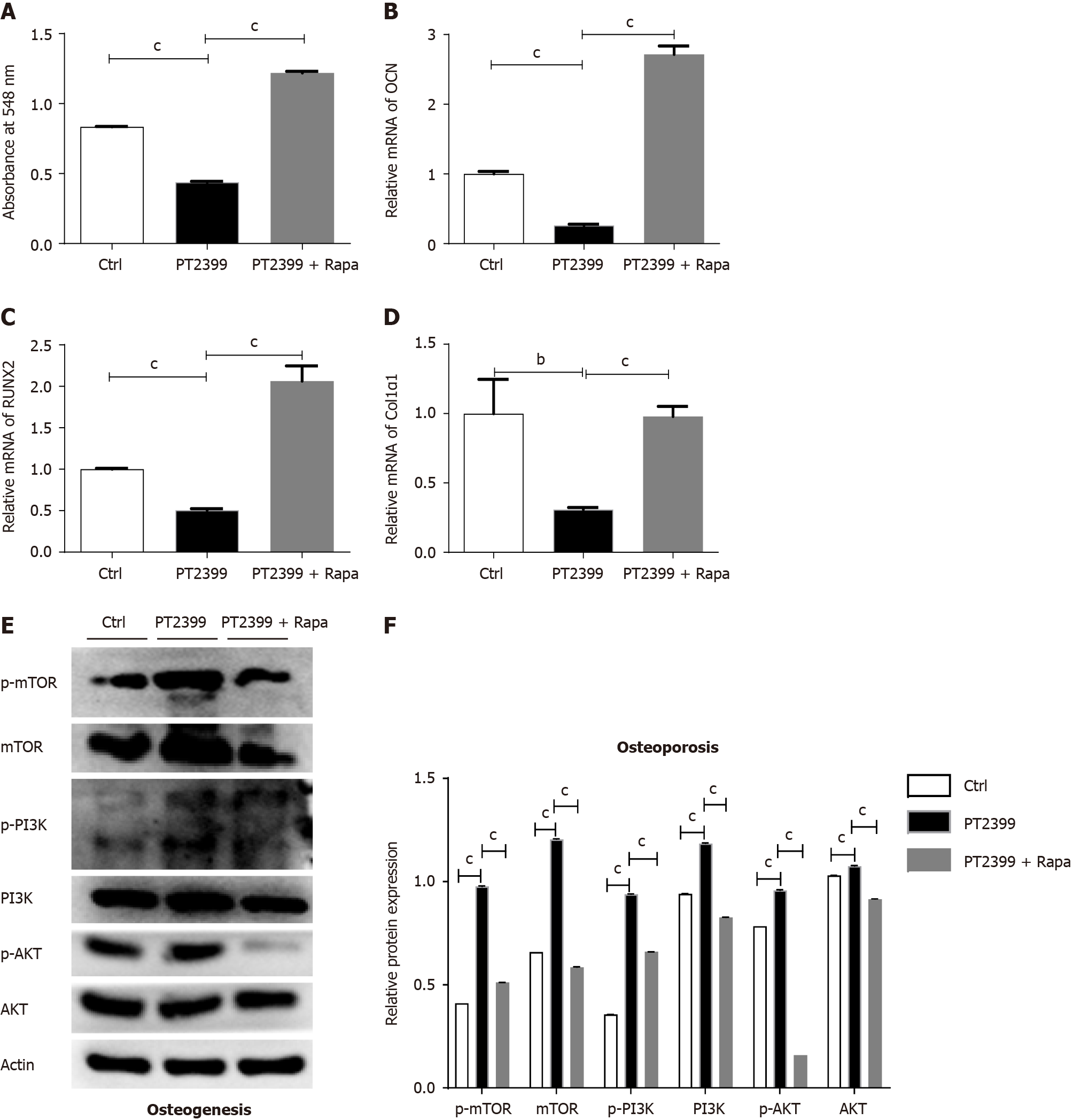
Figure 8 The mechanistic target of rapamycin inhibitor rapamycin rescued the decrease in the osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells induced by the hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha inhibitor PT2399.
A-F: Osteogenic differentiation was induced in Hif-2αfl/fl bone mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) by treatment with 10 μM PT2399 and 100 nM rapamycin for 14 d: Quantification of alizarin red staining in BMSCs after induction of osteogenic differentiation (A); relative mRNA expression levels of the osteogenesis-related genes OCN (B), RUNX2 (C) and Col1α1 (D) in BMSCs cells with induction of osteogenic differentiation with PT2399 and the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor rapamycin. Protein levels were measured by western blotting in the PT2399 and PT2399 + rapamycin groups (E). Quantification of the relative p-mTOR, mTOR, p-PI3K, PI3K, p-AKT and AKT levels (F). The phosphorylated protein levels were normalized to the corresponding total protein levels. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. Rapa: Rapamycin; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin.
- Citation: Wang LL, Lu ZJ, Luo SK, Li Y, Yang Z, Lu HY. Unveiling the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha in osteoporosis: Implications for bone health. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(4): 389-409
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i4/389.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.389