Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2024; 16(4): 389-409
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.389
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.389
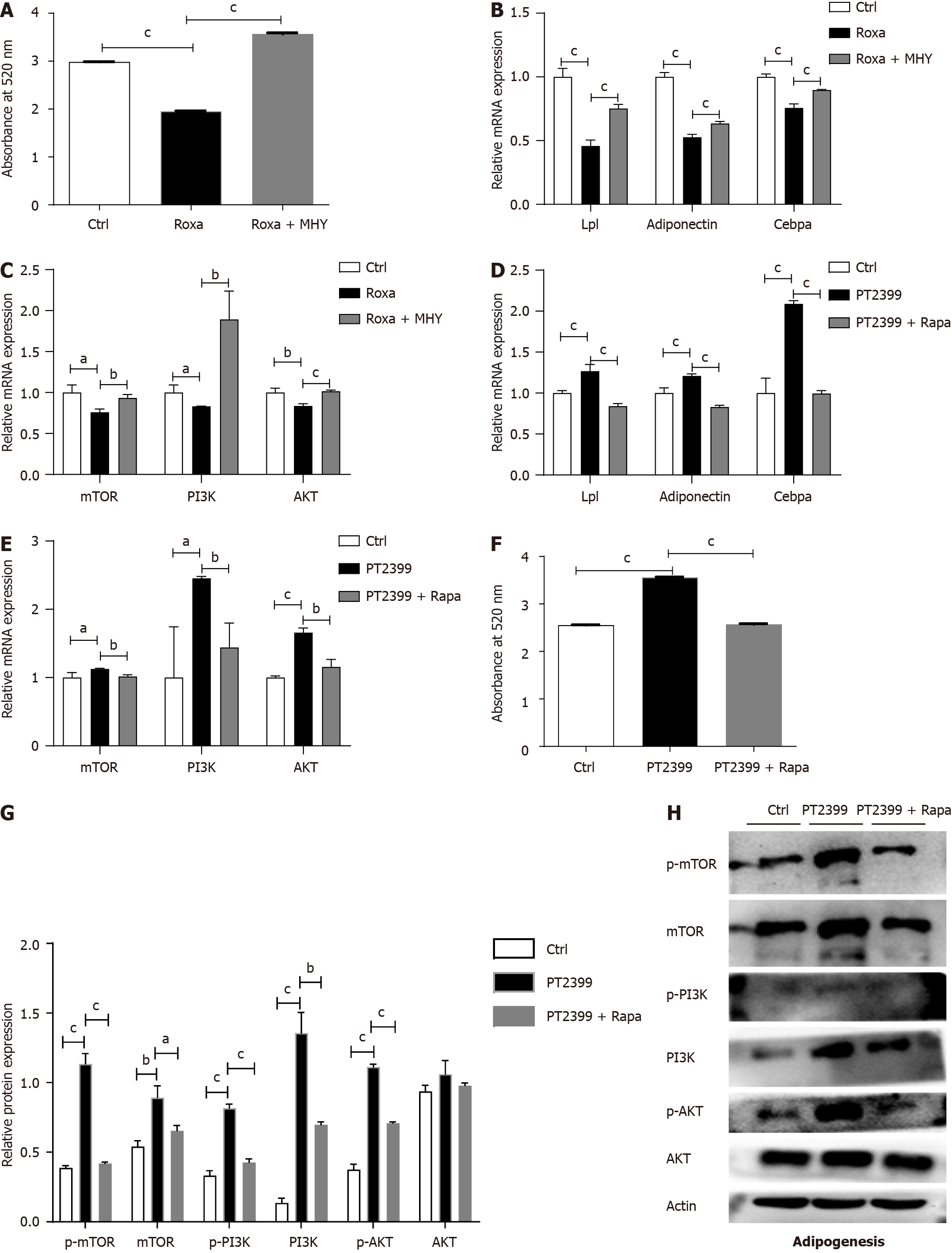
Figure 7 Hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha decreases bone mesenchymal stem cell adipogenic differentiation by inhibiting mechanistic target of rapamycin and PI3K/AKT signaling.
Adipogenic differentiation was induced in Hif-2αfl/fl bone mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) by treatment with roxadustat and MHY1485 for 7 d. A: Quantification of Oil Red O staining in BMSCs after induction of adipogenic differentiation; B: Relative mRNA expression levels of the adipogenesis-related genes Lpl, Adiponectin and Cebpα in BMSCs during adipogenic differentiation; C-G:: Relative mRNA expression levels of the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling-related genes mTOR, PI3K and AKT in BMSCs during adipogenic differentiation (C) Adipogenic differentiation was induced in BMSCs by treatment with 10 μM PT2399 and 100 nM rapamycin for 7 d; quantification of Oil Red O staining in BMSCs after induction of adipogenic differentiation (F); relative mRNA expression levels of adipogenesis-related genes in BMSCs with induction of osteogenic differentiation with PT2399 and the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin (D). Relative mRNA expression levels of mTOR signaling-related genes in BMSCs with induction of adipogenic differentiation with PT2399 and rapamycin (E). Protein levels were measured by western blotting in the PT2399 and PT2399 + rapamycin groups (H). Quantification of the relative p-mTOR, mTOR, p-PI3K, PI3K, p-AKT and AKT levels. The phosphorylated protein levels were normalized to the corresponding total protein levels (G). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. Roxa: roxadustat, MHY: MHY1485, Rapa: Rapamycin; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin.
- Citation: Wang LL, Lu ZJ, Luo SK, Li Y, Yang Z, Lu HY. Unveiling the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha in osteoporosis: Implications for bone health. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(4): 389-409
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i4/389.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.389