Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Mar 26, 2024; 16(3): 267-286
Published online Mar 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i3.267
Published online Mar 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i3.267
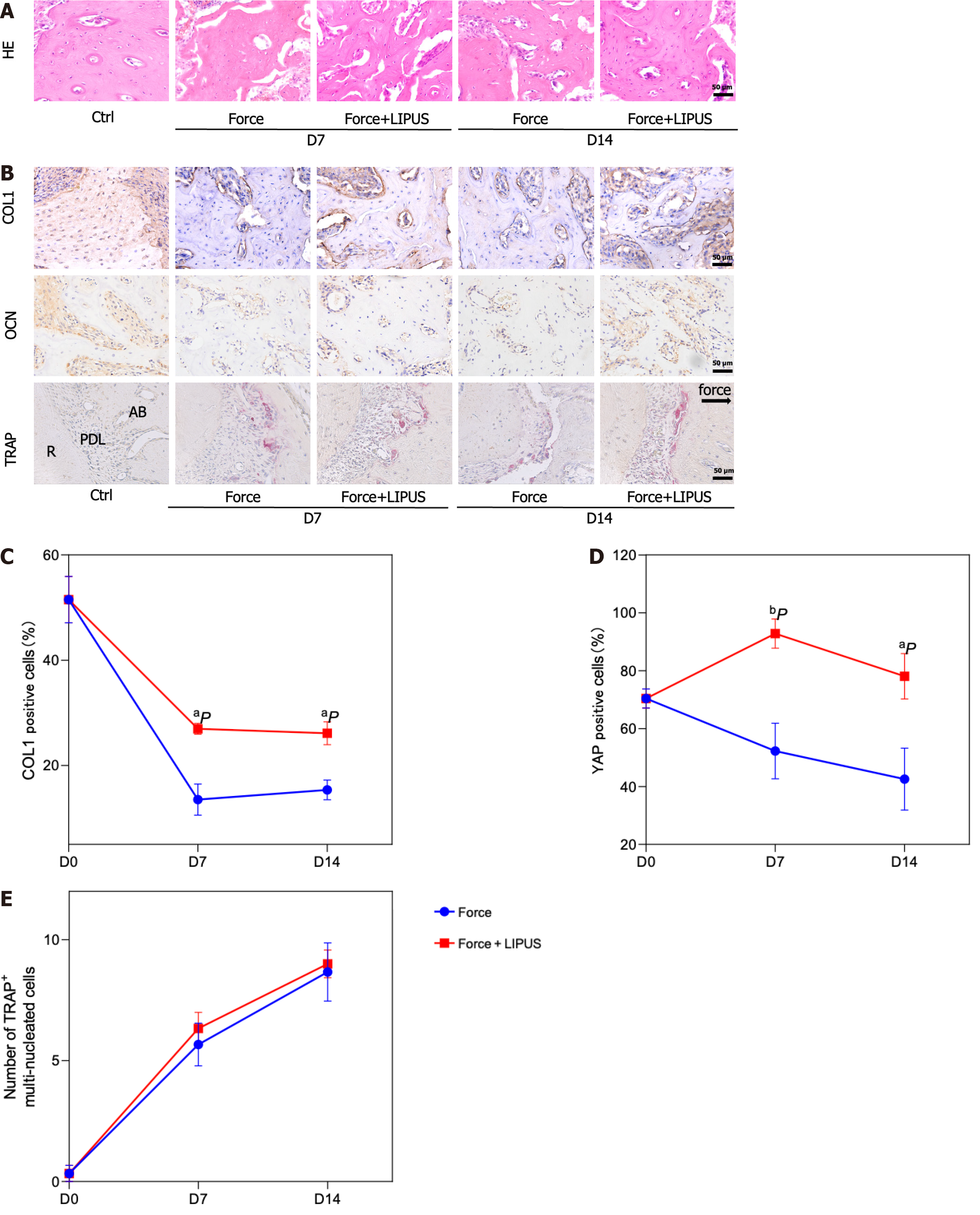
Figure 5 Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes bone formation.
A: Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin staining; B: Representative images of immunohistochemical staining for type 1 collagen and osteocalcin and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase staining (TRAP); C-E: Statistical analyses of the immunohistochemical staining and TRAP staining results. aP < 0.05 vs control group, bP < 0.01 vs control group. HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; TRAP: Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase; COL1: Type 1 collagen; OCN: Osteocalcin; LIPUS: Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound.
- Citation: Wu T, Zheng F, Tang HY, Li HZ, Cui XY, Ding S, Liu D, Li CY, Jiang JH, Yang RL. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound reduces alveolar bone resorption during orthodontic treatment via Lamin A/C-Yes-associated protein axis in stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(3): 267-286
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i3/267.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i3.267