Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2024; 16(2): 207-227
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.207
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.207
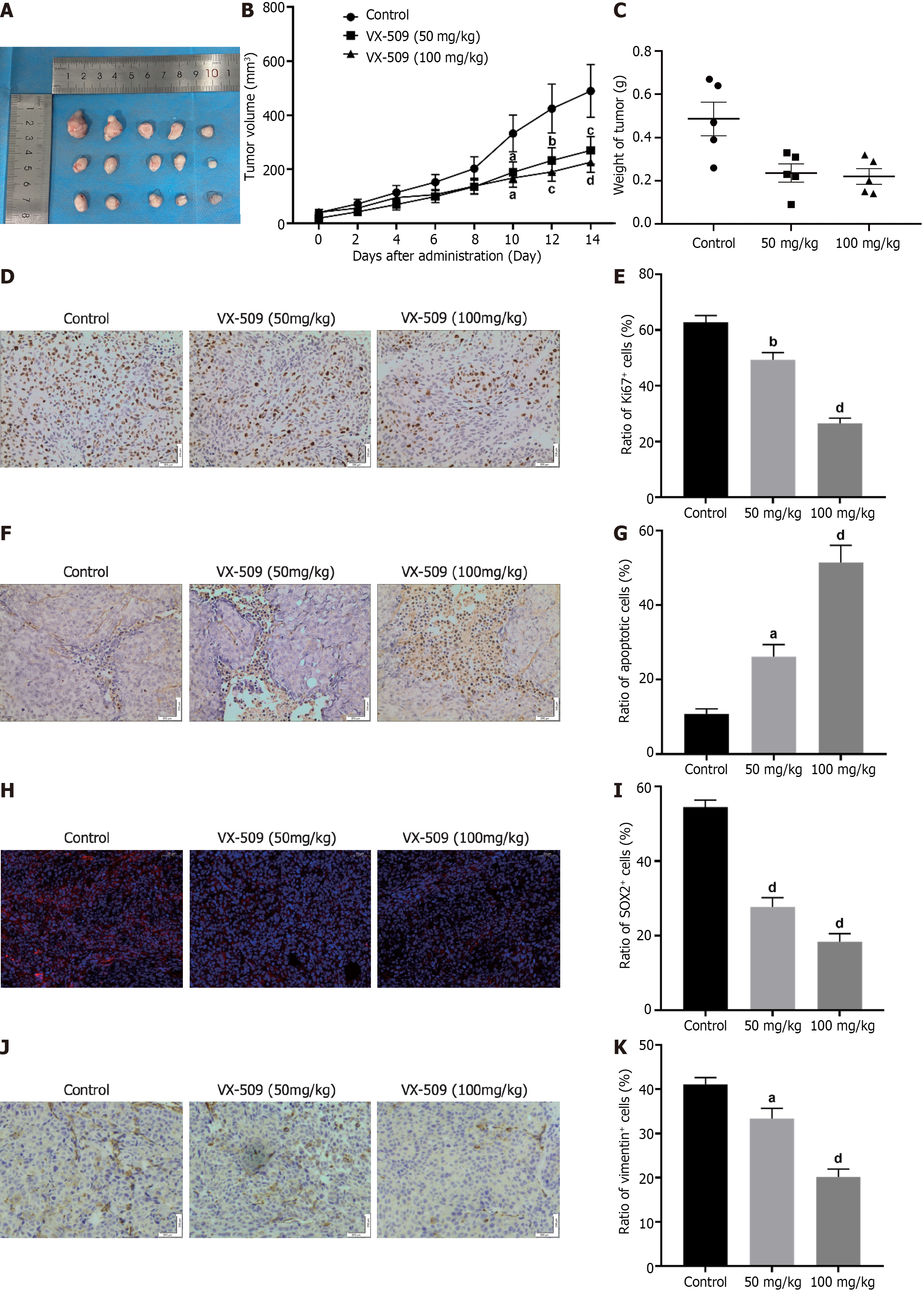
Figure 4 Anticancer efficacy of VX-509 against xenografts derived from colorectal cancer-derived cancer stem cells.
A: Tumors derived from HCT116 cancer stem cell (CSC)-bearing nude mice after 14 d of VX-509 treatment; B and C: The statistics of tumor volumes (B) and tumor weights (C) from HCT116 CSC-bearing nude mice treated with VX-509; D-K: Representative immunohistochemical images of Ki67 (D), TUNEL (F) and vimentin (J) as well as the mean of the IODs of Ki67 (E), TUNEL (G) and vimentin (K) in tumors from HCT116 CSC-bearing nude mice treated with VX-509 are shown. Representative immunofluorescent images of SOX2 (H) as well as the mean of the IOD of SOX2 (I) of tumors from HCT116 CSCs bearing nude mice treated with VX-509 are shown. Scale bars = 50 or 200 μm. n = 5. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001 compared to the control group.
- Citation: Yuan Y, Zhang XF, Li YC, Chen HQ, Wen T, Zheng JL, Zhao ZY, Hu QY. VX-509 attenuates the stemness characteristics of colorectal cancer stem-like cells by regulating the epithelial-mesenchymal transition through Nodal/Smad2/3 signaling. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(2): 207-227
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i2/207.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.207