Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2024; 16(2): 207-227
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.207
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.207
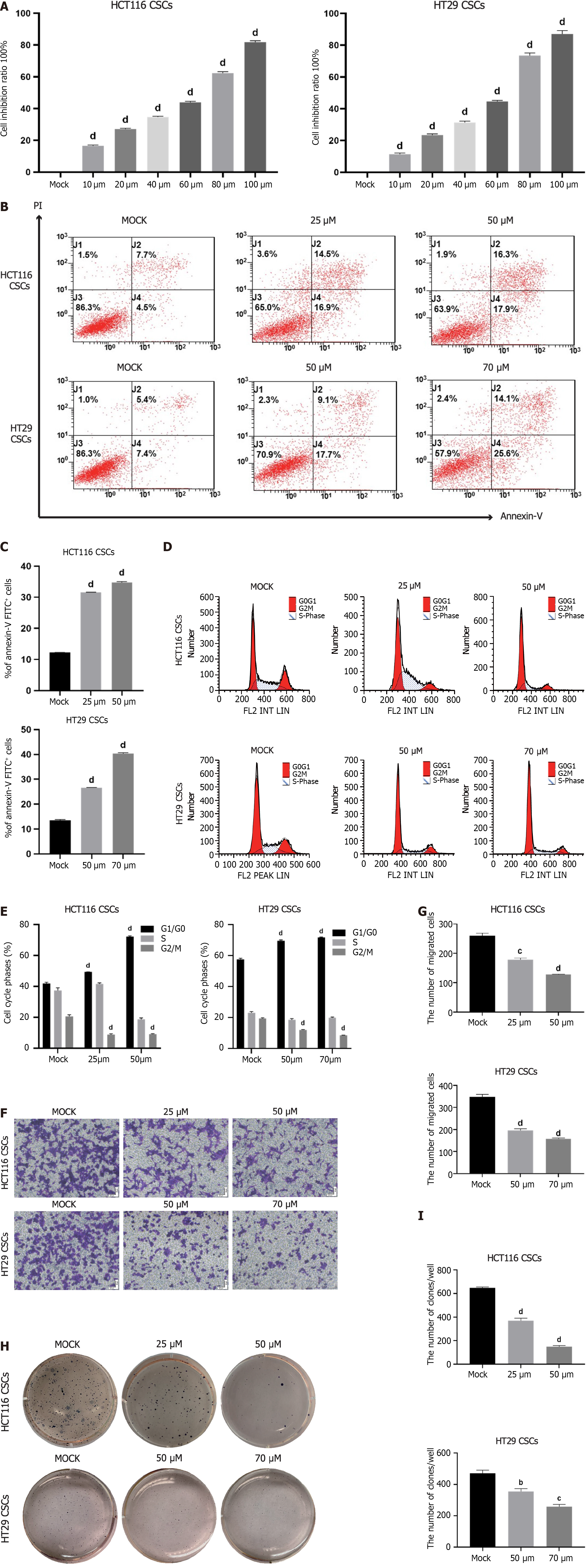
Figure 2 VX-509 inhibits the growth, migration, invasion and clonogenicity of colorectal cancer-derived cancer stem cells.
A: The viability of colorectal cancer-derived cancer stem cells (CSCs) treated with different concentrations of VX-509 was measured by a cell counting kit-8 assay; B and C: Flow cytometry analysis of early and late apoptotic rates and relative statistical analysis; D: Cell cycle distribution was measured using flow cytometry; E: Histograms of the proportions of G0/G1-, S- and G2/M-phase cells; F and G: The effects of different concentrations of VX-509 on the migration of HCT116 CSCs and HT29 CSCs detected by transwell assays and relative statistical analysis; H and I: The effects of different concentrations of VX-509 on the proliferation and tumorigenesis of HCT116 CSCs and HT29 CSCs detected by soft agar colony formation assays and relative statistical analysis. Scale bar = 50 μm. n = 3. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001 compared to the HCT116 cancer stem cells Mock group and HT29 cancer stem cells Mock group. CSC: Cancer stem cell.
- Citation: Yuan Y, Zhang XF, Li YC, Chen HQ, Wen T, Zheng JL, Zhao ZY, Hu QY. VX-509 attenuates the stemness characteristics of colorectal cancer stem-like cells by regulating the epithelial-mesenchymal transition through Nodal/Smad2/3 signaling. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(2): 207-227
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i2/207.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.207