Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2024; 16(2): 151-162
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.151
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.151
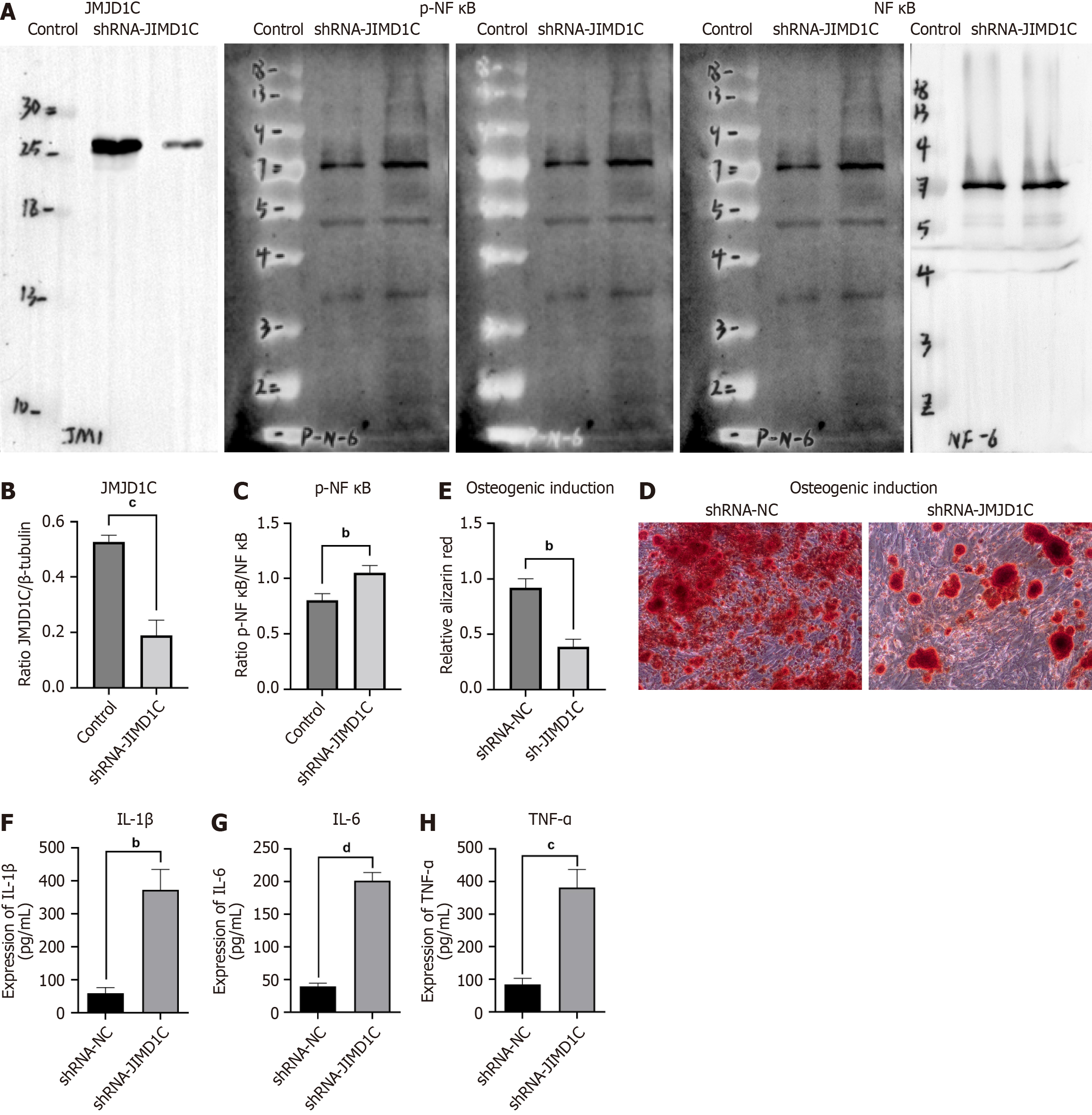
Figure 3 Jumonji domain-containing 1C knockdown inhibited osteogenic differentiation and upregulated p-nuclear factor-κB expression in bone mesenchymal stem cells.
Bone mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) were transfected with sh-NC or short hairpin RNA against Jumonji domain-containing 1C (sh-JMJD1C). A-C: Western blot was adopted to measure JMJD1C and p-nuclear factor-κB protein levels; D and E: Detection of osteogenic differentiation ability of BMSCs using alizarin red staining; F-H: Cytokines secretion level of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. All values are shown as mean ± SD. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001, n = 3. JMJD1C: Jumonji domain-containing 1C; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin; NF-κB: nuclear factor-κB.
- Citation: Li JY, Wang TT, Ma L, Zhang Y, Zhu D. Silencing of Jumonji domain-containing 1C inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via nuclear factor-κB signaling. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(2): 151-162
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i2/151.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.151