Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2024; 16(2): 137-150
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.137
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.137
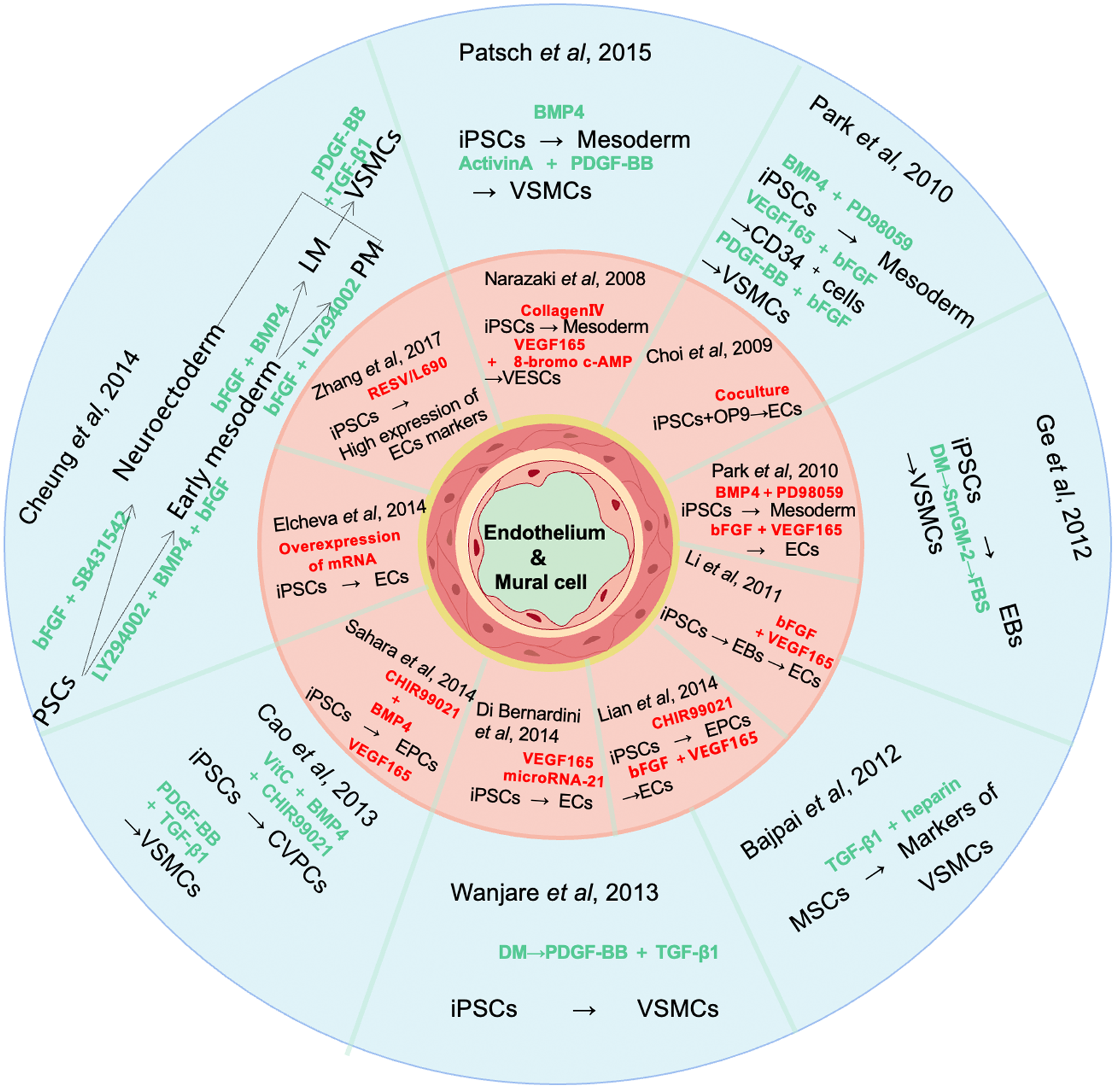
Figure 1 Modeling methods for endothelial cells and mural cells.
Several methods for differentiating induced pluripotent cell into endothelial cells and mural cells have been developed. The procedures of these modeling strategies are presented here as a schematic drawing. The inner ring shows the modeling strategies for endothelial cells, while the outer ring shows those for mural cells. The complementary factors and differentiation nodes are the focus of this graph. VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; TGF: Transforming growth factor; iPSC: Induced pluripotent cell; VSMC: Vascular smooth muscle cell; EB: Embryoid body; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; DM: Differentiation medium; CVPC: Cardiovascular progenitor cell; LM: Lateral mesoderm; PM: Paraxial mesoderm; VESC: Vascular endothelial stem cells; EC: Endothelial cell; EPC: Endothelial progenitor cell; BMP4: Bone morphogenetic protein 4; PDGF-BB: Platelet-derived growth factor-BB; FBS: Fetal bovine serum; bFGF: Basic fibroblast growth factor.
- Citation: Jiao YC, Wang YX, Liu WZ, Xu JW, Zhao YY, Yan CZ, Liu FC. Advances in the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into vascular cells. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(2): 137-150
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i2/137.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.137