Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2024; 16(2): 114-125
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.114
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.114
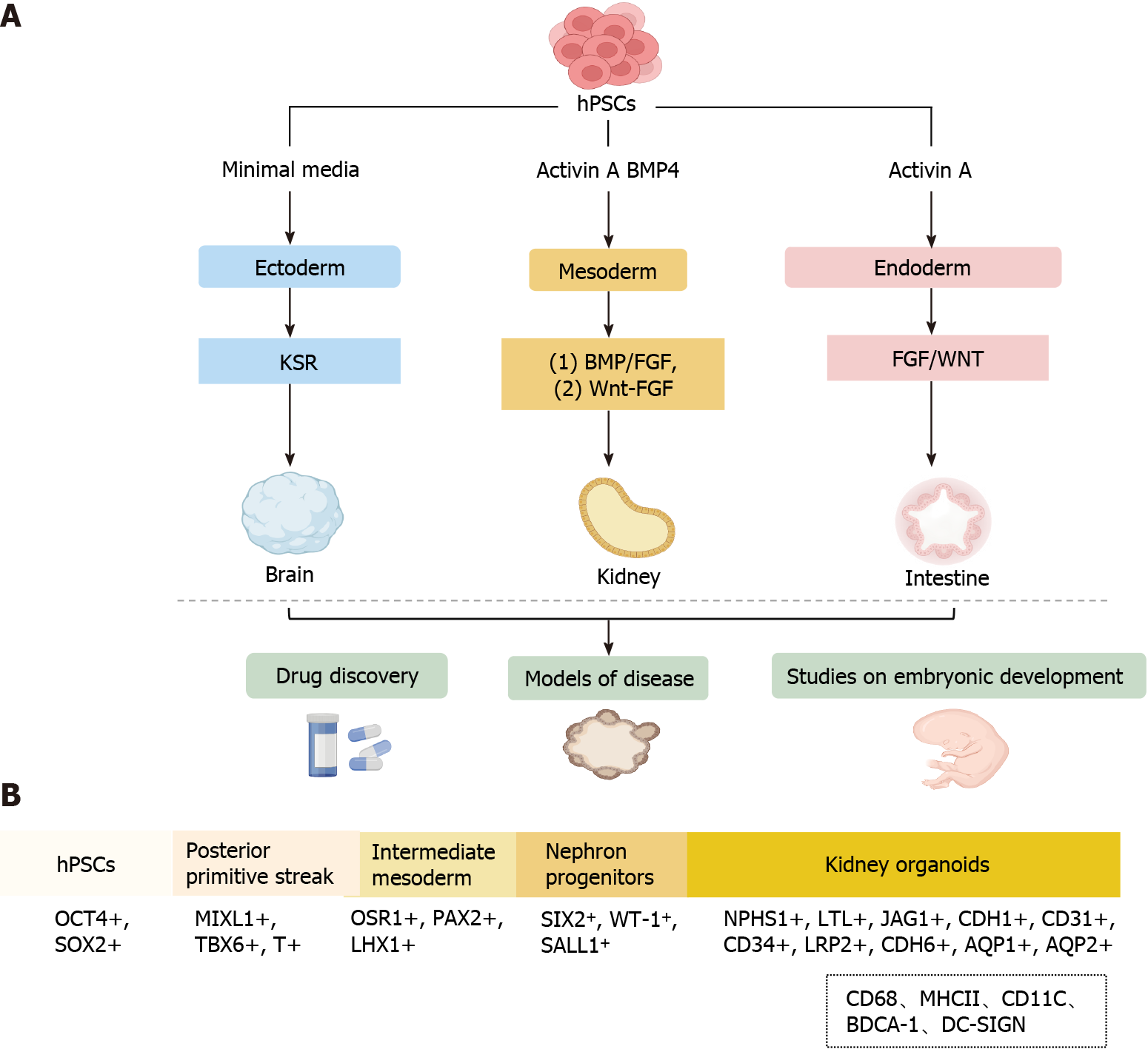
Figure 1 Overview of human pluripotent stem cell-derived organoids.
A: Schematic signaling of endodermal, mesodermal, and ectodermal triodermal organoids derived from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) by addition of different inducing factors; B: The process of generating hPSCs-derived kidney organoids involves the following consecutive stages: Generation of the posterior primitive streak, intermediate mesoderm, nephron progenitor cells, and kidney organoids. The dotted box shows immune cells not currently induced in kidney organoids in vitro. hPSCs: Human pluripotent stem cells; HSR: Knockout serum replacement; MHCII: Major histocompatibility complex; BDCA: Blood dendritic cell antigen; BMP: Bone morphogenetic protein; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor.
- Citation: Long HY, Qian ZP, Lan Q, Xu YJ, Da JJ, Yu FX, Zha Y. Human pluripotent stem cell-derived kidney organoids: Current progress and challenges. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(2): 114-125
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i2/114.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.114