Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2024; 16(2): 102-113
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.102
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.102
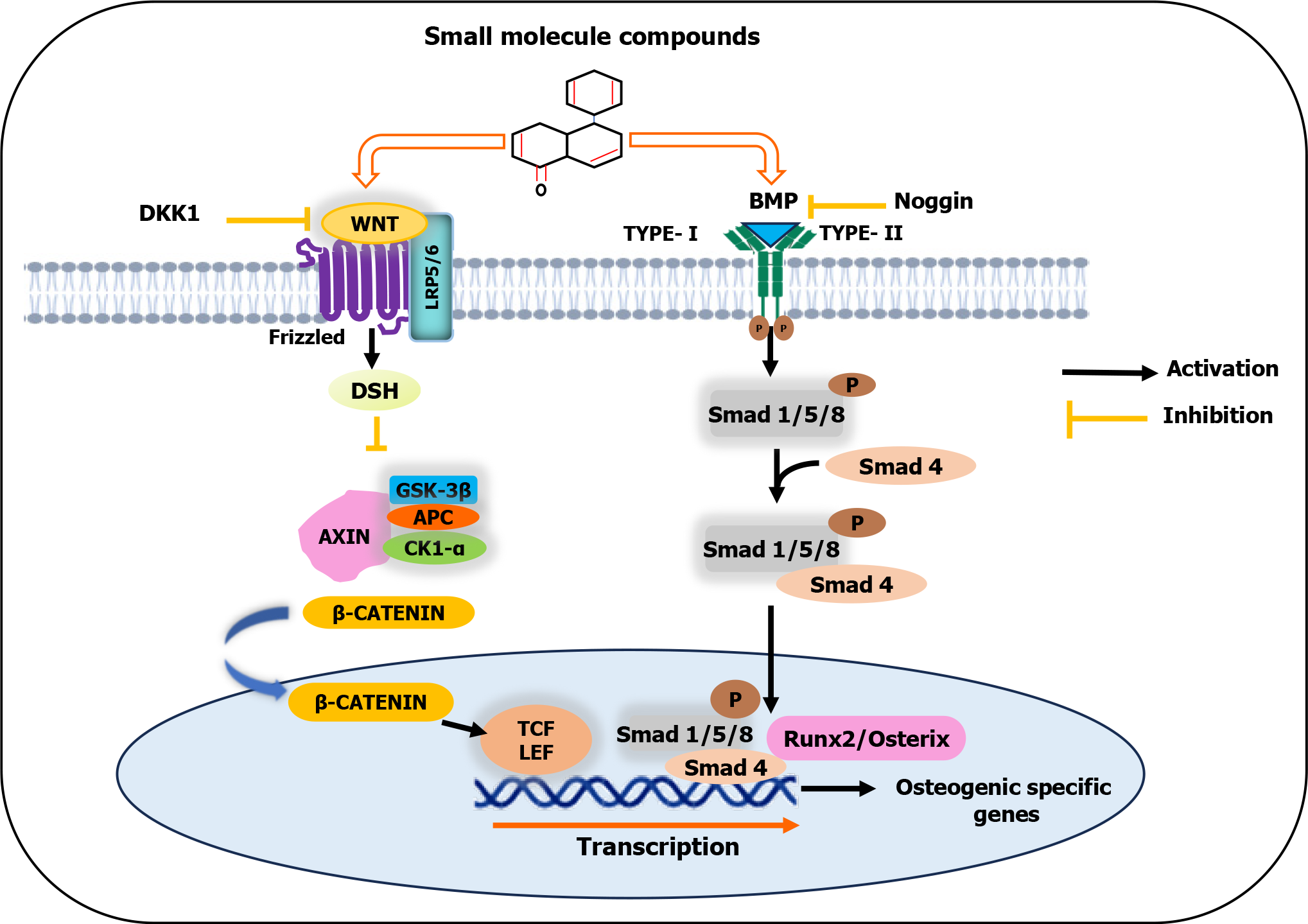
Figure 2 Schematic illustration of small molecule compounds inducing the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.
Small molecule compounds stimulate the bone morphogenetic protein signaling pathway and promote β-catenin accumulation. Then, β-catenin migrates to the nucleus and forms a β-catenin-T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor complex to initiate the transcription of genes associated with osteogenesis. GSK-3β: Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; APC: Adenomatosis polyposis coli; CK1-α: Casein kinase 1α; DSH: Disheveled; TCF/LEF: T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor; DKK1: Dickkopf 1; LRP5/6: Lipoprotein receptor-related proteins 5 or 6; BMP: Bone morphogenetic protein.
- Citation: Arya PN, Saranya I, Selvamurugan N. Crosstalk between Wnt and bone morphogenetic protein signaling during osteogenic differentiation. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(2): 102-113
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i2/102.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.102