Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2024; 16(2): 102-113
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.102
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.102
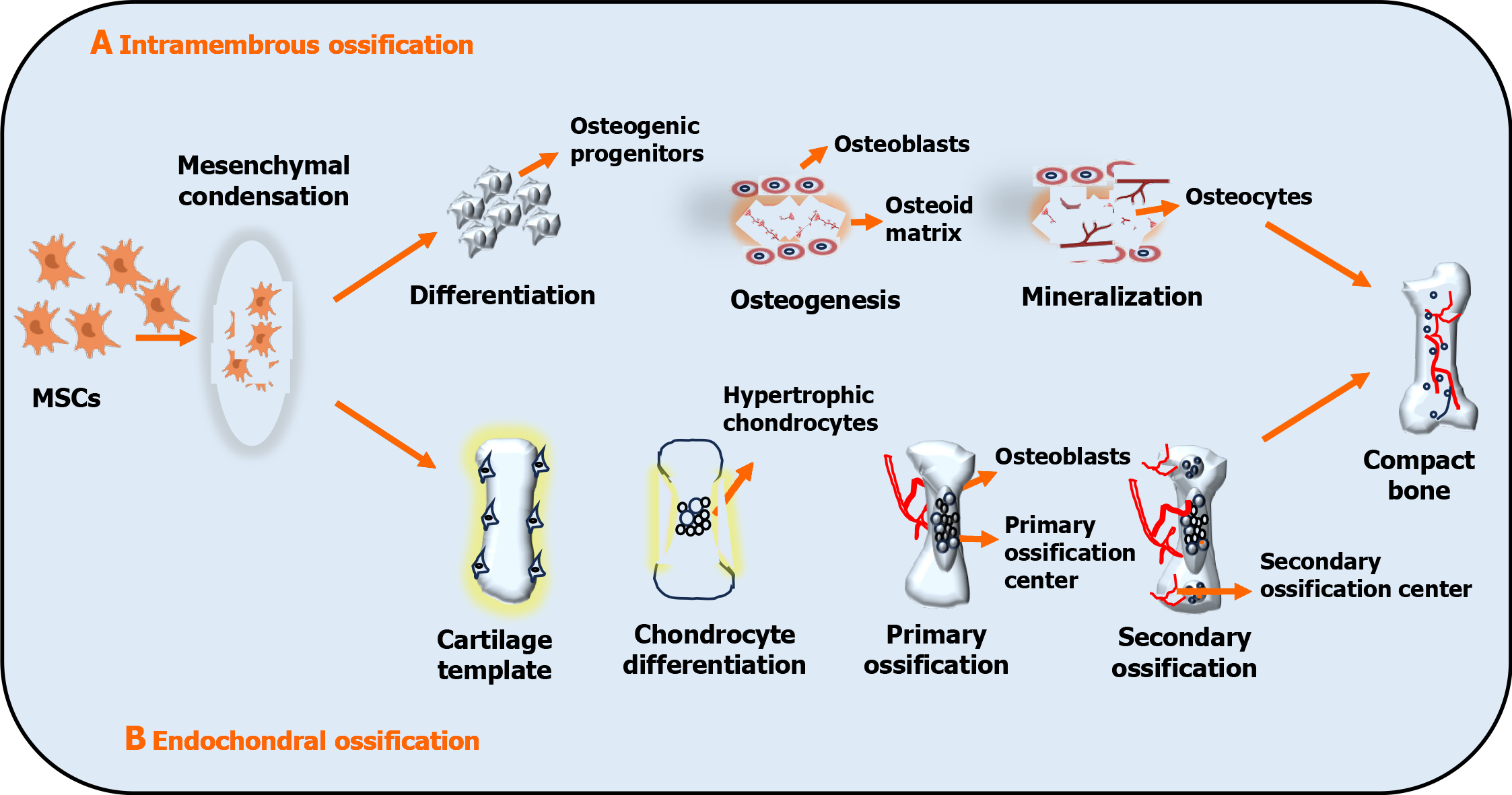
Figure 1 Schematic representation of intramembranous and endochondral ossification.
A: Undifferentiated mesenchymal cells develop into osteoprogenitor cells (osteoblasts), which lay down the osteoid matrix and mineralize to form ossification centers. Osteoblasts die due to apoptosis or become trapped in the matrix, developing into osteocytes; B: Condensed mesenchymal cells commit to become the cartilage and undergo chondrogenic differentiation. Chondrocytes at the primordium core establish a growth plate and undergo hypertrophy. Hypertrophic chondrocytes calcify and are penetrated by microvessels, resulting in primary ossification. Vessels infiltrate the epiphyses and produce secondary ossification centers in conjunction with osteoblasts and bone marrow. The growth plate aids in long bone formation. MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells.
- Citation: Arya PN, Saranya I, Selvamurugan N. Crosstalk between Wnt and bone morphogenetic protein signaling during osteogenic differentiation. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(2): 102-113
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i2/102.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.102