Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2024; 16(11): 944-955
Published online Nov 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i11.944
Published online Nov 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i11.944
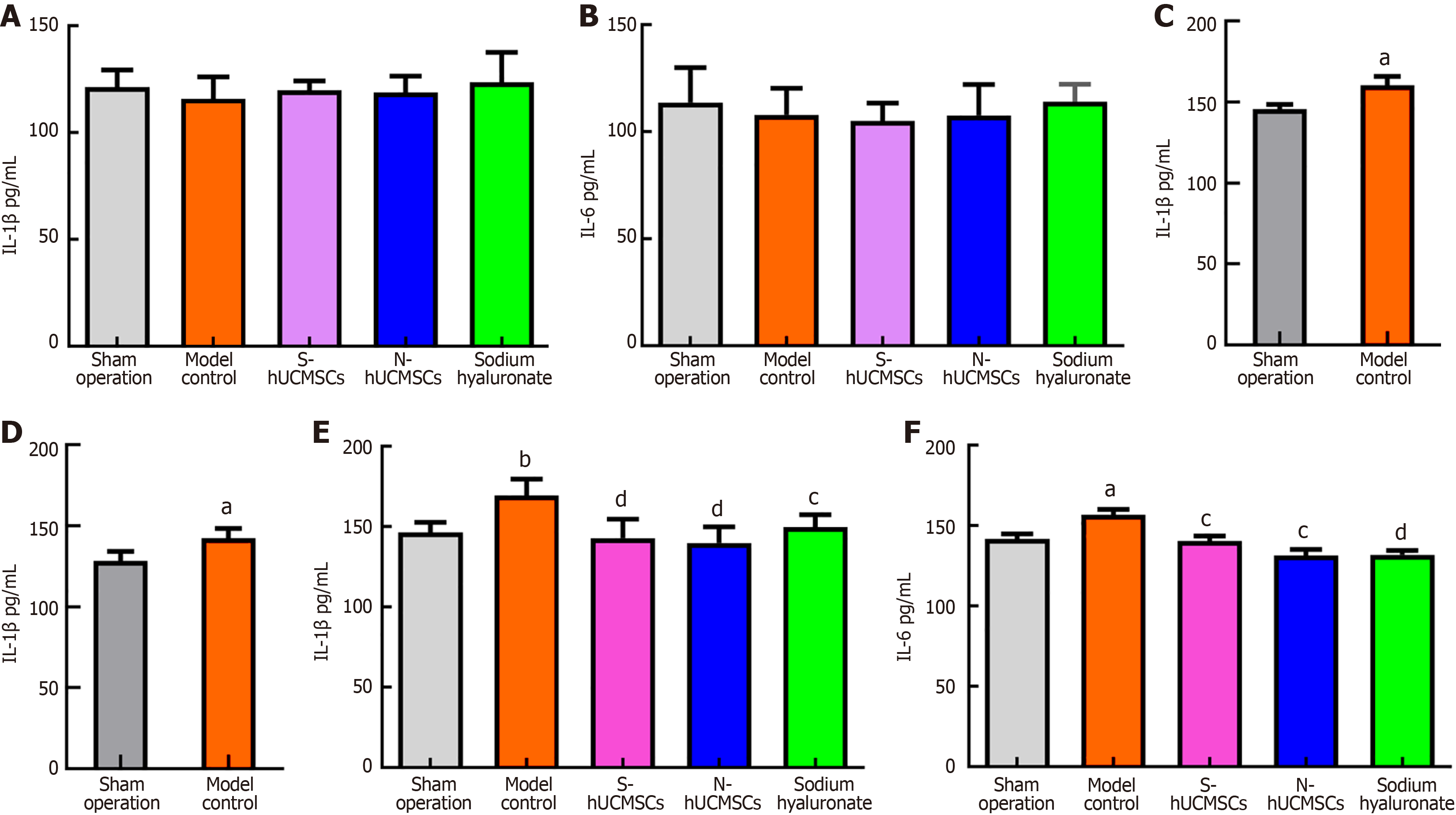
Figure 3 Reduced interleukin-6 and interleukin-1β expression in the experimental group.
A: Baseline analysis: There was no statistically significant difference in the initial levels of interleukin (IL)-1β among the groups of animals; B: Baseline analysis: There was no statistically significant difference in the initial levels of IL-6 among the groups of animals; C: Model validation: The level of IL-1β in the model control group was significantly higher than that in the sham surgery group (blank control group); D: Model validation: The level of IL-6 in the model control group was significantly higher than that in the sham surgery group (blank control group); E: Experimental endpoints: The level of IL-1β in the experimental group was significantly higher than that in the model control group; F: Experimental endpoints: The level of IL-6 in the experimental group was significantly higher than that in the model control group. aP < 0.05, comparison with the sham operated group; bP < 0.01, comparison with the sham operated group; cP < 0.05, comparison with the model control group; dP < 0.01, comparison with the model control group. N-hUCMSCs: Serum-free human umbilical cord mesenchymal stems; S-hUCMSCs: Serum-cultured human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Xiao KZ, Liao G, Huang GY, Huang YL, Gu RH. Efficacy of serum-free cultured human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis in mice. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(11): 944-955
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i11/944.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i11.944